VLOOKUP from another sheet in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate VLOOKUP from another sheet in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=VLOOKUP(lookup,sheet!range,column,match)
Explanation
Using VLOOKUP from another sheet is very similar to using VLOOKUP on the same sheet.
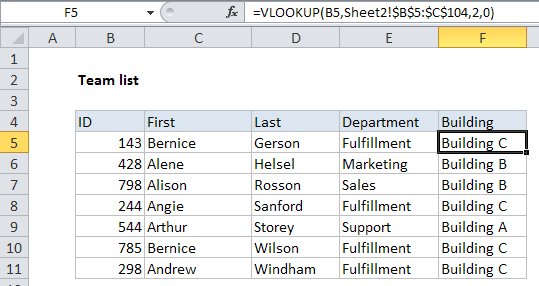
In the example shown, the formula in F5 is:
=VLOOKUP(B5,Sheet2!$B$5:$C$104,2,0)
Here, VLOOKUP pulls the correct building for each employee on Sheet2, into the table on Sheet1.
How this formula works
In this example, we have a list of employee locations like this on Sheet2:
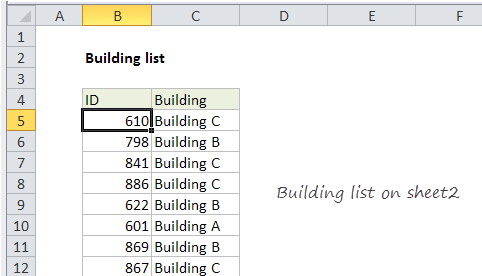
On Sheet1, we retrieve the building location for each team member using this formula:
=VLOOKUP(B5,Sheet2!$B$5:$C$104,2,0)
For lookup value, we simply use the value in column B, the employee id.
For the table array, we we use the range B54:$C$104 qualified with a sheet name:
Sheet2!$B$5:$C$104 // includes sheet name
This is the only difference from a standard VLOOKUP formula — including the sheet name simply tells VLOOKUP which sheet to use for the table lookup range.
Finally, column number is 2, since the building names appear in the second column, and VLOOKUP is set to exact match mode by including zero as the forth argument. This ensures that we get the correct building for each team member and a #N/A error if for some reason the id is not found in the location table.