How to use Excel NOT Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the NOT function with syntax and examples.
Excel NOT Function Description
The Excel NOT function returns the opposite to a supplied logical value.
That is,
- If supplied with the value TRUE, the Not function returns FALSE;
- If supplied with the value FALSE, the Not function returns TRUE.
Excel Not Function Examples
The following spreadsheet shows examples of the Excel Not Function.
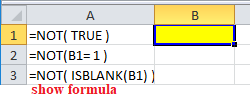
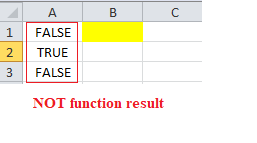
Explanation: Firstly, recall that NOT function returns the opposite to a supplied logical value
Cell A3 in the example above uses Excel Isblank function with the Not function, to test if cell B1 is blank.
Syntax
The syntax for the NOT function in Microsoft Excel is:
NOT( logical_value )
Arguments
- logical_value
- An expression that either evaluates to TRUE or FALSE. If used with an expression of TRUE, then FALSE is returned. If used with an expression of FALSE, then TRUE is returned.
Returns
If the logical_value is TRUE, then the NOT function will return FALSE.
If the logical_value is FALSE, then the NOT function will return TRUE.
Note that, if the supplied logical argument is a numeric value, zero is treated as the logical value FALSE and any other numeric value is treated as the logical value TRUE.