How to get last row in numeric data in Excel
To get the last relative position (i.e. last row, last column) for numeric data (with or without empty cells), you can use the MATCH function with a so called “big number”. see example below:
Formula
=MATCH(bignum,range)
Explanation
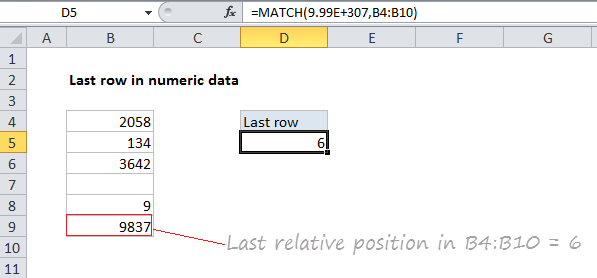
In the example shown, the formula in E5 is:
=MATCH(9.99E+307,B4:B9)
Last *relative* position, not row on worksheet
When building advanced formulas that create dynamic ranges, it’s often necessary to figure out the last location of data in a list. Depending on the data, this could be the last row with data, the last column with data, or the intersection of both. Note: we want the last *relative position* inside a given range, not the row number on the worksheet:
How this formula works
This formula uses the MATCH function in approximate match mode to locate the last numeric value in a range. Approximate match enabled by setting by the 3rd argument in MATCH to 1, or omitting this argument, which defaults to 1.
The lookup value is a so-called “big number” (sometimes abbreviated “bignum”) which is intentionally larger than any value that will appear in the range.
The result is that MATCH will “step back” to the last numeric value in the range, and return that position.
Note: this approach works fine with empty cells in the range, but is not reliable with mixed data that includes both numbers and text.
About bignum
The biggest number Excel can handle is 9.99999999999999E+307.
When using MATCH this way, you can use any large number that is guaranteed to be larger than any value in the range, for example:
=MATCH(1E+06,range) // 1 million =MATCH(1E+09,range) // 1 billion =MATCH(1E+12,range) // 1 trillion
The advantage to using 9.99E+307 or similar, is that it’s (1) a huge number and (2) recognizable as a placeholder for a “big number”.