Get work hours between dates and times in Excel
To calculate total work hours between two dates and times, you can use a formula based on the NETWORKDAYS function.
Formula
=(NETWORKDAYS(start,end)-1)*(upper-lower) +IF(NETWORKDAYS(end,end),MEDIAN (MOD(end,1),upper,lower),upper) -MEDIAN(NETWORKDAYS(start,start) *MOD(start,1),upper,lower)
Explanation
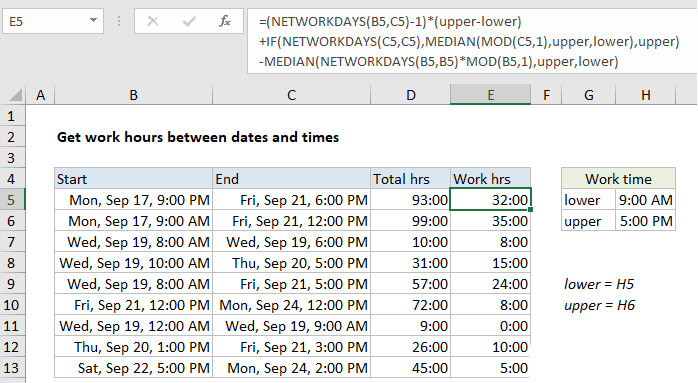
In the example shown, E5 contains this formula:
=(NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5)-1)*(upper-lower) +IF(NETWORKDAYS(C5,C5),MEDIAN (MOD(C5,1),upper,lower),upper) -MEDIAN(NETWORKDAYS(B5,B5) *MOD(B5,1),upper,lower)
where “lower” is the named range H5 and “upper” is the named range H6.
How this formula works
This formula calculates total working hours between two dates and times, that occur between a “lower” and “upper” time. In the example shown, the lower time is 9:00 AM and the upper time is 5:00 PM. These appear in the formula as the named ranges “lower” and “upper”.
The logic of the formula is to calculate all possible working hours between the start and end dates, inclusive, then back out any hours on the start date that occur between the start time and lower time, and any hours on the end date that occur between the end time and the upper time.
The NETWORKDAYS function handles the exclusion of weekends and holidays (when provided as a range of dates). You can switch to NETWORKDAYS.INTL if your schedule has non-standard working days.
Alternatively
If start and end times will always occur between lower and upper times, you can use a simpler version of this formula:
=(NETWORKDAYS(B5,C5)-1)*(upper-lower) +MOD(C5,1)-MOD(B5,1)
No start time and end time
To calculate total work hours between two dates, assuming all days are full workdays, you can use an even simpler formula:
=NETWORKDAYS(start,end,holidays)*hours