Excel Round a number down Example
If you need to round to force any number to round down, regardless of its value you can use the ROUNDDOWN function with a specified number of digits.
This tutorials shows how to Round a number down in Excel.
Formula
=ROUNDDOWN(number,digits)
Explanation
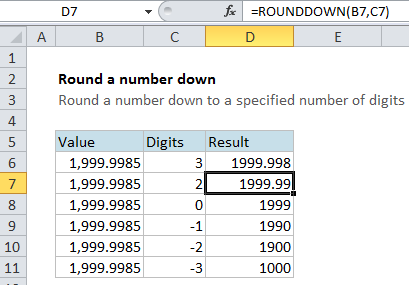
In the example, the formula in cell D7 is
=ROUNDDOWN(B7,C7)
This tells Excel to take the value in B7 (1999.9985) and round it to the number of digits in cell C7 (2) with a result of 1999.99
Notice that even though the number in the 3rd position to the right of the decimal is 8, it is still rounded down.
In the table, the ROUNDDOWN function is used to round the same number (1999.9985) to a decreasing number of digits, starting at 2 and moving down past zero to -3.
Note that positive numbers round to the right of the decimal point, while digits specified less than or equal to zero round to the left.
At each step, numbers that would normally be rounded up are rounded down.
You can see that ROUNDDOWN is a rather heavy handed function, so use it carefully.