Excel If, Nested If, And/Or Criteria Examples
IF function is one of the most used functions in Excel. This page contains many easy to follow IF examples.
Simple If Examples
The IF function checks whether a condition is met, and returns one value if true and another value if false.
1a. For example, take a look at the IF function in cell B2 below.
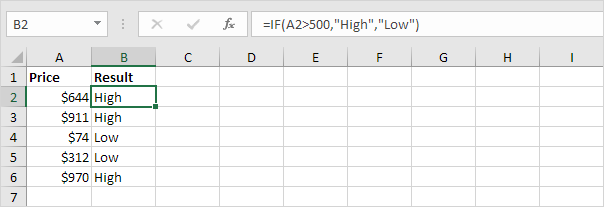
Explanation: if the price is greater than 500, the IF function returns High, else it returns Low.
1b. The following IF function produces the exact same result.

Note: you can use the following comparison operators: = (equal to), > (greater than), < (less than), >= (greater than or equal to), <= (less than or equal to) and <> (not equal to).
2. Always enclose text in double quotation marks.
3a. The formula below calculates the progress between two points in time.
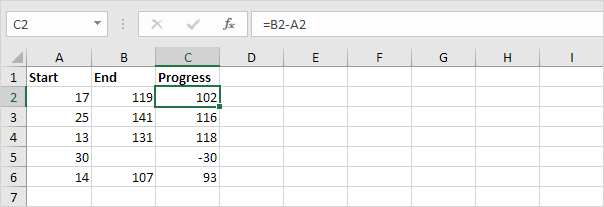
3b. You can use the IF function to display an empty string (“”) if the end value hasn’t been entered yet (see row 5).
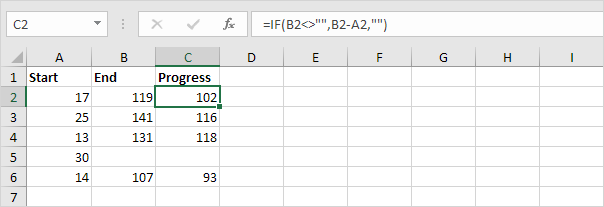
Explanation: if the end value is not empty (<> means not equal to), the IF function calculates the progress between the start and end value, else it displays an empty string (“”).
And/Or Criteria
Use the IF function in combination with the AND function and the OR function and become an Excel expert.
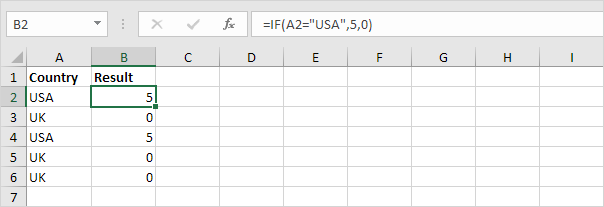
1. For example, take a look at the IF function in cell D2 below.
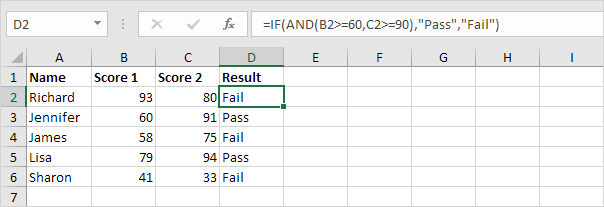
Explanation: the AND function returns TRUE if the first score is greater than or equal to 60 and the second score is greater than or equal to 90, else it returns FALSE. If TRUE, the IF function returns Pass, if FALSE, the IF function returns Fail.
2. For example, take a look at the IF function in cell D2 below.
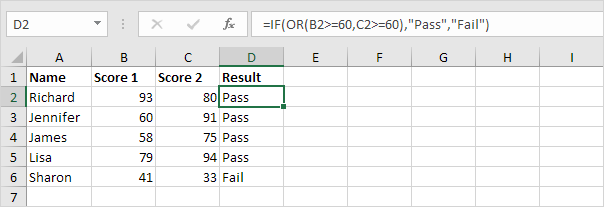
Explanation: the OR function returns TRUE if at least one score is greater than or equal to 60, else it returns FALSE. If TRUE, the IF function returns Pass, if FALSE, the IF function returns Fail.
3. For example, take a look at the IF function in cell D2 below.

Explanation: the AND function above has two arguments separated by a comma (Table, Green or Blue). The AND function returns TRUE if Product equals “Table” and Color equals “Green” or “Blue”. If TRUE, the IF function reduces the price by 50%, if FALSE, the IF function reduces the price by 10%.
Nested If
The IF function in Excel can be nested, when you have multiple conditions to meet. The FALSE value is being replaced by another IF function to make a further test.
1. For example, take a look at the nested IF formula in cell C2 below.
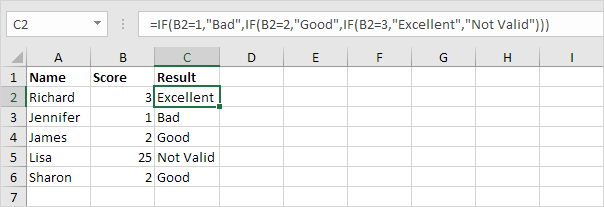
Explanation: if the score equals 1, the nested IF formula returns Bad, if the score equals 2, the nested IF formula returns Good, if the score equals 3, the nested IF formula returns Excellent, else it returns Not Valid. If you have Excel 2016, simply use the IFS function.
2. For example, take a look at the nested IF formula in cell C2 below.
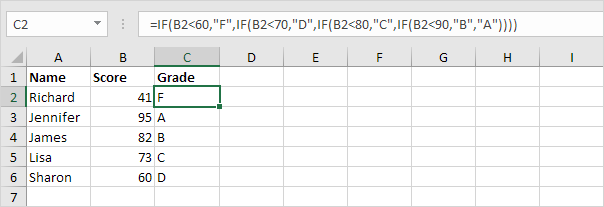
Explanation: if the score is less than 60, the nested IF formula returns F, if the score is greater than or equal to 60 and less than 70, the formula returns D, if the score is greater than or equal to 70 and less than 80, the formula returns C, if the score is greater than or equal to 80 and less than 90, the formula returns B, else it returns A.