Series of dates by day
This tutorials shows how to generates Series of dates increment by day from a single start date in Excel.
If you need to generate a dynamic series of dates with a formula that increase by one day from a single start date, you can do so a very simple formula that simply adds 1 to each date.
Formula
=date+1
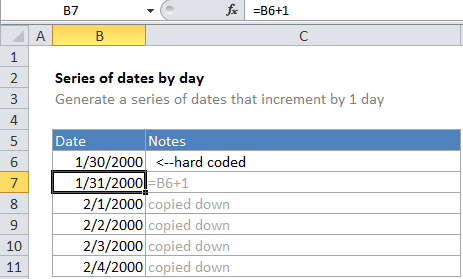
Explanation
In the example, B6 is the hard-coded start date and the formula in B7 is:
=B6+1
Because dates in Excel are just serial numbers (the first date in the standard Excel date system is January 1, 1900), you can adjust dates just adding or subtracting values. To solve this formula, Excel just adds 1 to the date in B6. The first formula therefore returns a new date of 1/31/2000, one day later than the starting date.
Once the first formula is entered, it is copied down as far as needed. Each subsequent formula creates a new date incremented by one day. You could easily adjust the formula generate future dates by weeks, by using 7 instead of 1, like so:
=B6+7