If cell contains one of many things in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate If cell contains one of many things in Excel using the example below;
Formula
{=INDEX(results,MATCH(TRUE,ISNUMBER
(SEARCH(things,A1)),0))}
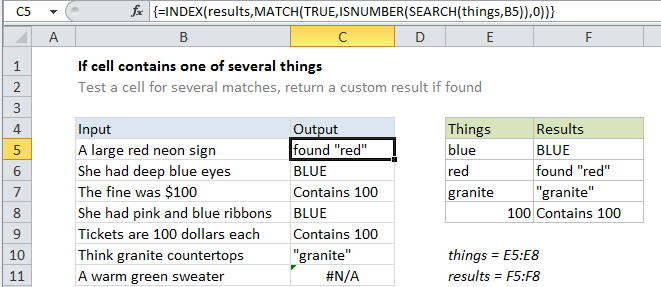
Explanation
To test a cell for one of several things, and return a custom result for the first match found, you can use an INDEX / MATCH formula based on the SEARCH function.
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
{=INDEX(results,MATCH(TRUE,
ISNUMBER(SEARCH(things,B5)),0))}
This is an array formula and must be entered with Control + Shift + Enter.
How this formula works
This formula uses two named ranges: E5:E8 is named “things”, and F5:F8 is named “results”. Make sure you use name ranges with the same names (based on your data). If you don’t want to use named ranges, use absolute references instead.
The core of this formula is this snippet:
ISNUMBER(SEARCH(things,B5)
This is based on another formula (explained in detail here) that checks a cell for a single substring. If the cell contains the substring, the formula returns TRUE. If not, the formula returns FALSE.
Because we give SEARCH more than one thing to look for, it will give us back a list of results, in an array that looks like this:
{#VALUE!;9;#VALUE!;#VALUE!}
To simply the array, we use the ISNUMBER function to convert all items in the array to either TRUE or FALSE. Any valid number becomes TRUE, and any error (i.e. a thing not found) becomes FALSE. The result is an array like this:
{FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE}
Which goes into the MATCH function as the “lookup_array”, with a “lookup_value” of TRUE.
MATCH then returns the position of first TRUE found (in this case is 2).
Finally, we use INDEX to retrieve a result from the named range “results” at that same position.
This approach lets you populate the “results” range with whatever values you want.
Preventing false matches
One problem with this approach with the ISNUMBER + SEARCH approach is you may get false matches from partial matches inside longer words. For example, if you try to match “dr” you may also find “Andrea”, “drank”, “drip”, etc. since “dr” appears inside these words. This happens because SEARCH automatically does a “contains-type” match.
For a quick fix, you can wrap search words in space characters (i.e. ” dr “, or “dr “) to avoid finding “dr” in another word. But this will fail if “dr” appears first or last in a cell.
If you need a more robust solution, one option is to normalize the text first in a helper column, and add a leading and trailing space. Then use the formula on this page on the text in the helper column, instead of the original text.