Convert date to Julian format in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Convert date to Julian format in Excel using example below.
If you need to convert a date to a Julian date format in Excel, you can do so by building a formula that uses the TEXT, YEAR, and DATE functions.
Formula
=YEAR(date)&TEXT(date-DATE(YEAR(date),1,0),"000")
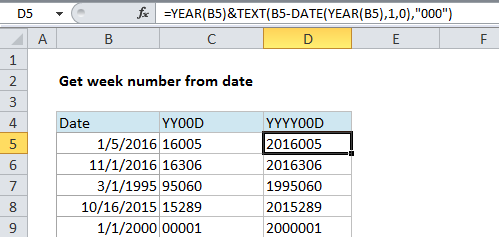
Explanation
Background
“Julian date format” refers to a format where the year value of a date is combined with the “ordinal day for that year” (i.e. 14th day, 100th day, etc.) to form a date stamp.
There are several variations. A date in this format may include a 4-digit year (yyyy) or a two-digit year (yy) and the day number may or may not be padded with zeros to always use 3 digits. For example, for the date January 21, 2017, you might see:
1721 // YYD 201721 //YYYYD 2017021 // YYYYDDD
Solution
For a two-digit year + a day number without padding use:
=TEXT(B5,"yy")&B5-DATE(YEAR(B5),1,0)
For a two-digit year + a day number padded with zeros to 3 places:
=TEXT(B5,"yy")&TEXT(B5-DATE(YEAR(B5),1,0),"000")
For a four-digit year + a day number padded with zeros to 3 places:
=YEAR(B5)&TEXT(B5-DATE(YEAR(B5),1,0),"000")
How this formula works
This formula builds the final result in 2 parts, joined by concatenation with the ampersand (&) operator.
On the left of the ampersand, we generate the year value. To extract a 2-digit year, we can use the TEXT function, which can apply a number format inside a formula:
TEXT(B5,"yy")
To extract a full year, use the YEAR function:
YEAR(B5)
On the right side of the ampersand we need to figure out the day of year. We do this by subtracting the last day of the previous year from the date we are working with. Because dates are just serial numbers, this will give us the “nth” day of year.
To get the last day of year of the previous year, we use the DATE function. When you give DATE a year and month value, and a zero for day, you get the last day of the previous month. So:
B5-DATE(YEAR(B5),1,0)
gives us the last day of the previous year, which is December 31, 2015 in the example.
Now we need to pad the day value with zeros. Again, we can use the TEXT function:
TEXT(B5-DATE(YEAR(B5),1,0),"000")
Reverse Julian date
If you need to convert a Julian date back to a regular date, you can use a formula that parses Julian date and runs it through the date function with a month of 1 and day equal to the “nth” day. For example, this would create a date from a yyyyddd Julian date like 1999143.
=DATE(LEFT(A1,4),1,RIGHT(A1,3)) // for yyyyddd
If you just have a day number (e.g. 100, 153, etc.), you can hard-code the year and insert the day this:
=DATE(2016,1,A1)
Where A1 contains the day number. This works because the DATE function knows how to adjust for values that are out of range.