Calculate payment for a loan in Excel
To calculate a loan payment amount, given an interest rate, the loan term, and the loan amount, you can use the PMT function.
Formula
=PMT(rate,periods,-amount)
Explanation
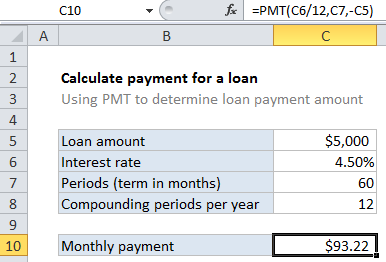
In the example shown, the formula in C10 is:
=PMT(C6/12,C7,-C5)
How this formula works
Loans have four primary components: the amount, the interest rate, the number of periodic payments (the loan term) and a payment amount per period. You can use the PMT function to get the payment when you have the other 3 components.
For this example, we want to find the payment for a $5000 loan with a 4.5% interest rate, and a term of 60 months. To do this, we configure the PMT function as follows:
rate – The interest rate per period. We divide the value in C6 by 12 since 4.5% represents annual interest, and we need the periodic interest.
nper – the number of periods comes from cell C7; 60 monthly periods for a 5 year loan.
pv – the loan amount comes from C5. We use the minus operator to make this value negative, since a loan represents money owed.
With these inputs, the PMT function returns 93.215, rounded to $92.22 in the example using the currency number format.