Excel Date & Time Functions Example
To enter a date in Excel, use the “/” or “-” characters. To enter a time, use the “:” (colon). You can also enter a date and a time in one cell.
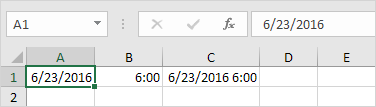
Note: Dates are in US Format. Months first, Days second. This type of format depends on your windows regional settings. Learn more about Date and Time formats.
Year, Month, Day
To get the year of a date, use the YEAR function.
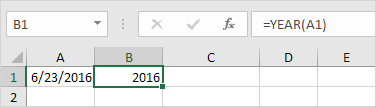
Note: use the MONTH and DAY function to get the month and day of a date.
Date Function
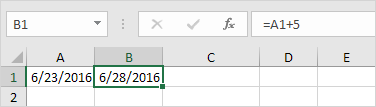
1. To add a number of days to a date, use the following simple formula.
2. To add a number of years, months and/or days, use the DATE function.
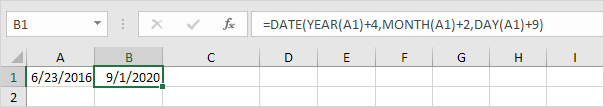
Note: the DATE function accepts three arguments: year, month and day. Excel knows that 6 + 2 = 8 = August has 31 days and rolls over to the next month (23 August + 9 days = 1 September).
Current Date & Time
To get the current date and time, use the NOW function.
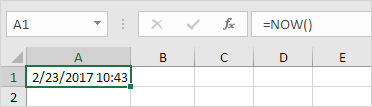
Note: use the TODAY function to enter today’s date in Excel.
Hour, Minute, Second
To return the hour, use the HOUR function.
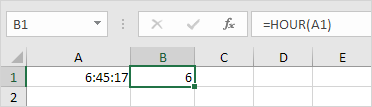
Note: use the MINUTE and SECOND function to return the minute and second.
Time Function
To add a number of hours, minutes and/or seconds, use the TIME function.
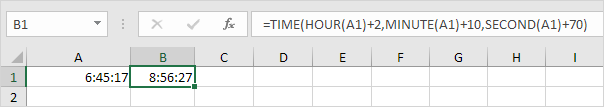
Note: Excel adds 2 hours, 10 + 1 = 11 minutes and 70 – 60 = 10 seconds.
