Convert Excel time to decimal seconds
This tutorial shows how to Convert Excel time to decimal seconds using example below.
To convert a valid Excel time into decimal seconds, you can multiply by 86400.
Formula
=A1*86400
Explanation
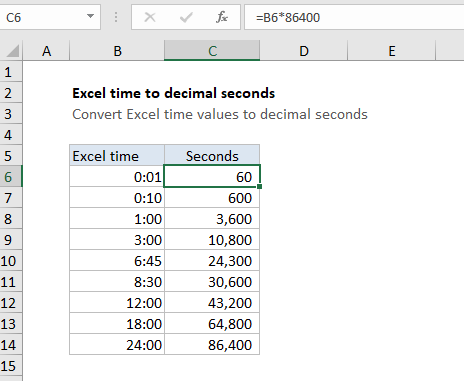
In the example shown, the formula in C6 is:
=B6*86400
which returns a value of 60, since there are 60 seconds in 1 minute.
How this formula works
In the Excel time system, one 24-hour day is equal to 1. This means times and hours are fractional values of 1, as shown in the table below:
| Hours | Time | Fraction | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:00 AM | 1/24 | 0.04167 |
| 3 | 3:00 AM | 3/24 | 0.125 |
| 6 | 6:00 AM | 6/24 | 0.25 |
| 4 | 4:00 AM | 4/24 | 0.167 |
| 8 | 8:00 AM | 8/24 | 0.333 |
| 12 | 12:00 PM | 12/24 | 0.5 |
| 18 | 6:00 PM | 18/24 | 0.75 |
| 21 | 9:00 PM | 21/24 | 0.875 |
Because each hour can be represented as 1/24, you can convert an Excel time into decimal hours by multiplying the value by 24, convert to decimal minutes by multiplying the value by 1440 (24 * 60) , and convert to seconds by multiplying by 86400 (24 * 60 * 60).
With the time value 6:00 cell A1, you can visualize the conversion like this:
=A1*(24*60*60) =(6/24)*86400 =0.25*86400 =21,600
The Excel time 6:00 converts to 21,600 seconds.