Round a number up to nearest multiple in Excel
This tutorials shows how to Round a number up to nearest multiple in Excel.
If you need to round a number up to the nearest specified multiple (i.e. round a number up to the nearest dollar, up to the nearest $.25, up to the nearest multiple of 5, etc.) you can use the CEILING function.
Formula
=CEILING(number,multiple)
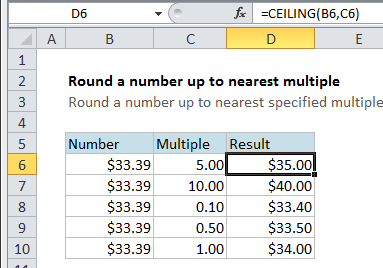
Explanation
In the example, the formula in cell D6 is
=CEILING(B6,C6)
This tells Excel to take the value in B6 ($33.39 ) and round it to the nearest multiple of the value in C6 (5). The result is $35.00, since 35 is the next multiple of 5 after 33.39. In cell D10, we are rounding the same number, 33.39 up to the nearest multiple of 1 and get 34.00.
You can use CEILING to round prices, times, instrument readings or any other numeric value.
Note that CEILING rounds up using the multiple supplied. You can use the MROUND function to round to the nearest multiple and the FLOOR function to round down to the nearest multiple.