Calculate shipping cost with VLOOKUP in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Calculate shipping cost with VLOOKUP in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=VLOOKUP(weight,table,column,1)*weight
Explanation
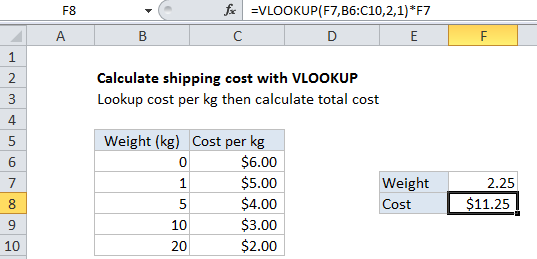
To calculate shipping cost based on weight, you can use the VLOOKUP function.
In the example shown, the formula in F8 is:
=VLOOKUP(F7,B6:C10,2,1)*F7
This formula uses the weight to find the correct “cost per kg” then calculates the final cost.
How this formula works
The core of the formula is VLOOKUP, which is configured in approximate match mode by setting the forth argument to 1 or TRUE.
In approximate match mode, the values in the first column of VLOOKUP must be sorted. VLOOKUP will return a value at the first row that is less than or equal to the lookup value.
With weight as the lookup value, VLOOKUP finds and returns the right cost per kg. This cost is then multiplied by the weight to calculate the final cost.
Adding a minimum charge
What if you business rules dictate a minimum shipping cost of $5.00, no matter what the weight? A clever way to handle this is to wrap the entire formula in the MAX function like so:
=MAX(VLOOKUP(F7,B6:C10,2,1)*F7,5)
Now max will return whichever is greater – the result of the formula or 5.