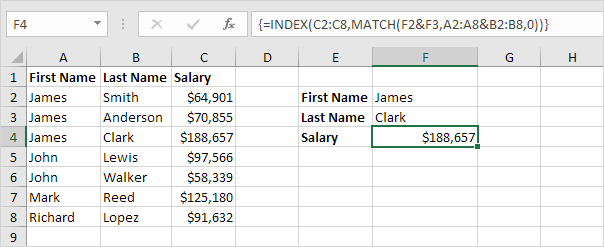
Two-column Lookup in Excel
This example teaches you how to perform a two-column lookup in Excel. See the example below. We want to look up the salary of James Clark, not James Smith, not James Anderson.
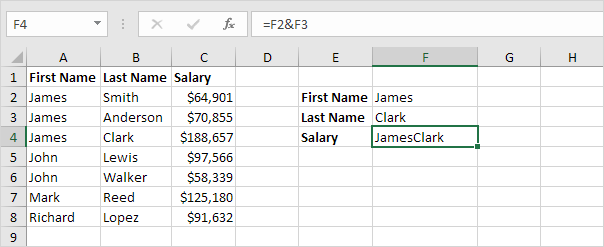
1. To join strings, use the & operator.
2. The MATCH function returns the position of a value in a given range. Insert the MATCH function shown below.
3. Finish by pressing CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER.
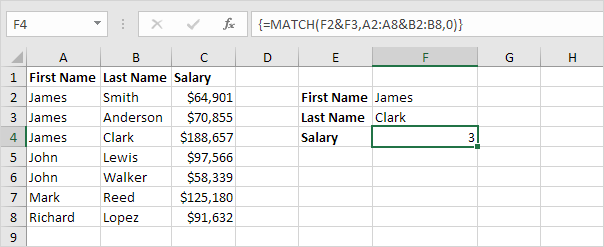
Note: The formula bar indicates that this is an array formula by enclosing it in curly braces {}. Do not type these yourself. They will disappear when you edit the formula.
Explanation: The range (array constant) A2:A8&B2:B8 is stored in Excel’s memory, not in a range. The array constant looks as follows:
{“JamesSmith”;”JamesAnderson”;”JamesClark”;”JohnLewis”;”JohnWalker”;”MarkReed”;”RichardLopez”}
This array constant is used as an argument for the MATCH function, giving a result of 3 (JamesClark found at position 3).
4. Use this result and the INDEX function to return the 3rd value in the range C2:C8.