Convert time to time zone in Excel
This tutorial show how to Convert time to time zone in Excel using the example below.
To convert a time from one time zone to another, you can use a formula that converts hours entered as whole numbers to the decimal values that Excel recognizes as times.
Formula
=MOD(time+(hours/24),1)
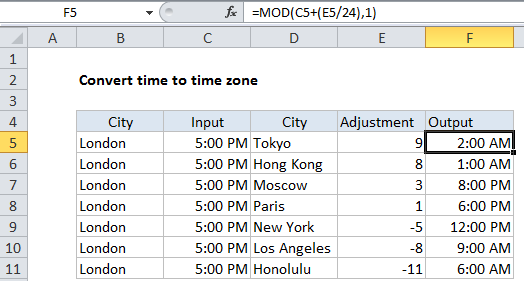
Explanation of how this formula works
In the example shown, the formula in F5 is:
=MOD(C5+(E5/24),1)
This formula returns a number that Excel recognizes as 2:00 AM.
Times in Excel are fractional values of the number 1. So, 12 PM is 12/24 = .5, 6:00 AM is 6/24 = .25, and so on. So, to convert a time by a given number, you need to divide the number of hours by 24 to get required decimal value:
E5/24 // convert adjustment to Excel time
We add the result to the starting time:
C5+(E5/24)
To make sure we have a true time value, we need to ensure that we have only a decimal value. In other words, if we add 12 hours (.5) to 6 PM (.75) we’ll get 1.25, but we really only want .25.
To make sure we get just the decimal value, we use MOD with a divisor of 1, as a clever way to keep the formula simple.
MOD returns the remainder after division, so returns the decimal value in cases where the result is greater than 1 (i.e. greater than 24 hours).
Even better, if we end up with a negative fractional value, MOD returns the reciprocal. So, if we end up with -.25, MOD returns .75 (equivalent to 6 PM).
This is important, because Excel won’t display negative time values.
Datetimes
Some date values include both a date and time, and are sometimes called “datetimes”. These values include both a serial number to represent the date plus a fractional value to represent time. The table below shows some examples:
| Datetime | Raw value |
|---|---|
| 3/6/18 6:00 AM | 43165.25 |
| 1-Jan-1999 21:00 | 36161.875 |
| 4/1/2020 0:00 | 43922 |
| June 3, 1980 12:00 PM | 29375.5 |
When working with dates that include both a date and time (datetimes), you don’t need to use MOD, because there’s no need to do anything clever as times cross midnight. The operation becomes simple addition, because the date is included, and you can use a formula like this:
=datetime+(hours/24)
This will allow the date value change as needed (forwards or backwards) when time adjustments cross 12:00 AM.