How to reference named range different sheet in Excel
This tutorials shows how to reference a named range on another sheet.
To achieve this, you can use the INDIRECT function with the required sheet syntax.
Formula
INDIRECT("'"&sheet&"'!"&name)
Explanation
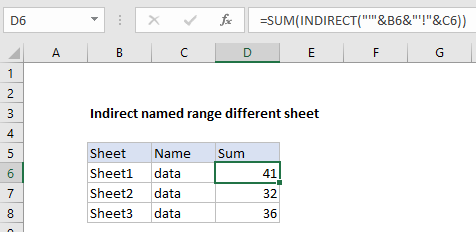
In the example shown, the formula in D6 is:
=SUM(INDIRECT("'"&B6&"'!"&C6))
Which returns the sum of the named range “data” on Sheet1.
How this formula works
The formula above evaluates something like this:
=SUM(INDIRECT("'"&B6&"'!"&C6))
=SUM(INDIRECT("'"&"Sheet1"&"'!"&"data"))
=SUM('Sheet1'!data)
Once the string is assembled using values in B6 and C6, INDIRECT evaluates and transforms the string into a proper reference.
Note you can refer to a named range in a formula without using INDIRECT. For example, the formula in D6 could be written:
=SUM('Sheet1'!data)
Note: The single quotes are added in the formula above so that the formula will work when a sheet name contains spaces.
However, if you want to assemble the reference as text, and have Excel treat the text as a reference, you need to use INDIRECT.