RECEIVED function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is RECEIVED function in Excel?
RECEIVED function is one of Financial functions in Microsoft Excel that returns the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security.
Syntax of RECEIVED function
RECEIVED(settlement, maturity, investment, discount, [basis])
The RECEIVED function syntax has the following arguments:
- Settlement: The security’s settlement date. The security settlement date is the date after the issue date when the security is traded to the buyer.
- Maturity: The security’s maturity date. The maturity date is the date when the security expires.
- Investment: The amount invested in the security.
- Discount: The security’s discount rate.
- Basis (Optional): The type of day count basis to use.
Note: Dates should be entered by using the DATE function, or as results of other formulas or functions. For example, use DATE(2008,5,23) for the 23rd day of May, 2008. Problems can occur if dates are entered as text.
| Basis | Day count basis |
| 0 or omitted | US (NASD) 30/360 |
| 1 | Actual/actual |
| 2 | Actual/360 |
| 3 | Actual/365 |
| 4 | European 30/360 |
RECEIVED formula explanation
- Microsoft Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers so they can be used in calculations. By default, January 1, 1900 is serial number 1, and January 1, 2008 is serial number 39448 because it is 39,448 days after January 1, 1900.
- The settlement date is the date a buyer purchases a coupon, such as a bond. The maturity date is the date when a coupon expires. For example, suppose a 30-year bond is issued on January 1, 2008, and is purchased by a buyer six months later. The issue date would be January 1, 2008, the settlement date would be July 1, 2008, and the maturity date would be January 1, 2038, which is 30 years after the January 1, 2008, issue date.
- Settlement, maturity, and basis are truncated to integers.
- If settlement or maturity is not a valid date, RECEIVED returns the #VALUE! error value.
- If investment ≤ 0 or if discount ≤ 0, RECEIVED returns the #NUM! error value.
- If basis < 0 or if basis > 4, RECEIVED returns the #NUM! error value.
- If settlement ≥ maturity, RECEIVED returns the #NUM! error value.
- RECEIVED is calculated as follows:
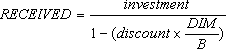 where:
where:
- B = number of days in a year, depending on the year basis.
- DIM = number of days from issue to maturity.
Example of RECEIVED function
Steps to follow:
1. Open a new Excel worksheet.
2. Copy data in the following table below and paste it in cell A1
Note: For formulas to show results, select them, press F2 key on your keyboard and then press Enter.
You can adjust the column widths to see all the data, if need be.
| Data | Description | |
| 15-Feb-08 | Settlement (issue) date | |
| 15-May-08 | Maturity date | |
| $ 1,000,000.00 | Investment | |
| 5.75% | Percent discount rate | |
| 2 | Actual/360 basis | |
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =RECEIVED(A2,A3,A4,A5,A6) | The total amount to be received at maturity, for the bond with the terms in A2:A6. | $ 1,014,584.65 |