How to calculate present value of annuity in excel
To get the present value of an annuity, you can use the PV function.
Formula
=PV(rate,periods,payment,0,0)
In the example shown, the formula in C9 is:
=PV(C5,C6,C4,0,0)
Explanation
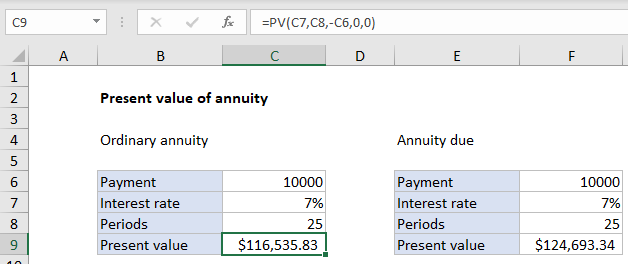
An annuity is a series of equal cash flows, spaced equally in time. In this example, an annuity pays 10,000 per year for the next 25 years, with an interest rate (discount rate) of 7%. To calculate present value, the PV function is configured as follows:
- nper – the value from cell C8, 25.
- pmt – the value from cell C6, 100000.
- rate – the value from cell C7, 7%.
- fv – 0.
- type – 0, payment at end of period (regular annuity).
With this information, the present value of the annuity is $116,535.83. Note payment is entered as a negative number, so the result is positive.
Annuity due
With an annuity due, payments are made at the beginning of the period, instead of the end. To calculate present value for an annuity due, use 1 for the type argument. In the example shown, the formula in F9 is:
=PV(F7,F8,-F6,0,1)
Note the inputs (which come from column F) are the same as the original formula. The only difference is type = 1.