Two ways to sum time over 30 minutes in Excel
To sum the total amount of time over 30 minutes, given a set of times that represent duration, you can use the SUMPRODUCT and TIME functions. Alternatively, use SUMIFS and COUNTIFS functions.
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT((range-TIME(0,30,0))*(range>TIME(0,30,0)))
Explanation
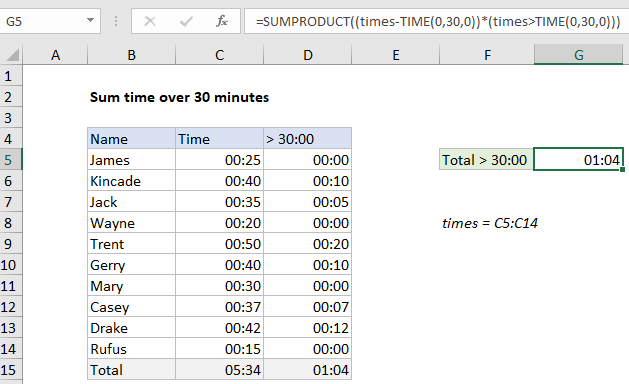
In the example shown, the formula in G5 is:
=SUMPRODUCT((times-TIME(0,30,0))*(times>TIME(0,30,0)))
where “times” is the named range C5:C14.
How this formula works
This formula uses the SUMPRODUCT function to sum the result of two expressions that yield arrays. The goal is to sum only time greater than 30 minutes, the “surplus” or “extra” time. The first expression subtracts 30 minutes from every time in the named range “times”:
times-TIME(0,30,0)
This results in an array like this:
{-0.00347222222222222;0.00694444444444444;0.00347222222222222;-0.00694444444444444;0.0138888888888889;0.00694444444444444;0;0.00486111111111111;0.00833333333333333;-0.0104166666666667}
The second expression is a logical test for all times greater than 30 minutes:
times>TIME(0,30,0)
This creates an array of TRUE FALSE values:
{FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;FALSE}
Inside SUMPRODUCT, these two arrays are multiplied together to create this array:
{0;0.00694444444444444;0.00347222222222222;0;0.0138888888888889;0.00694444444444444;0;0.00486111111111111;0.00833333333333333;0}
Notice negative values in the first array are now zeros. During multiplication, the TRUE FALSE values are converted to 1 and zero, so FALSE values “cancel out” times that are not greater than 30 min. Finally, SUMPRODUCT returns the sum of all values in the array, 1 hour and 4 minutes (1:04).
Alternative with SUMIFS and COUNTIFS
By itself, SUMIFS cannot sum the delta of time values greater than 30 minutes. SUMIFS and COUNTIFS can be used together to get the same result as SUMPRODUCT above:
=SUMIFS(times,times,">0:30")-(COUNTIFS(times,">0:30")*"0:30")
Times over 24 hours
If total times may exceed 24 hours, use this a custom time format like this:
[h]:mm:ss
The square bracket syntax tells Excel not to “roll over” times greater than 24 hours.
With a helper column
As shown in the example, you can also add a helper column to calculate and sum time deltas. The formula in D5, copied down, is:
=MAX(C5-"00:30",0)
Here, MAX is used to get rid of negative time deltas, caused by times in column C that are less than 30 minutes. Notice the result in D15 is the same as the result in G5.