Calculate number of hours between two times in Excel
This tutorials shows how to calculate number of hours between two times in Excel.
To calculate the number of hours between two times, you can use a formula that simply subtracts the start time from the end time. This is useful to calculate working time, calculate elapsed time, etc. However, when times cross a day boundary (midnight), things can get tricky.
Formula
=end-start
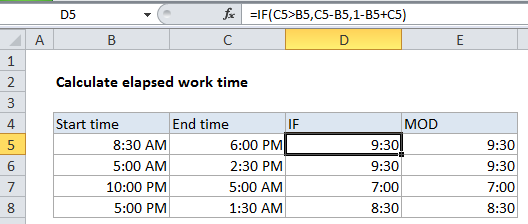
Explanation
In Excel, one day equals 1, which represents 24 hours. This means times and hours are fractional values of 1, as shown in the table below:
| Hours | Time | Fraction | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3:00 AM | 3/24 | 0.125 |
| 6 | 6:00 AM | 6/24 | 0.25 |
| 4 | 4:00 AM | 4/24 | 0.167 |
| 8 | 8:00 AM | 8/24 | 0.333 |
| 12 | 12:00 PM | 12/24 | 0.5 |
| 18 | 6:00 PM | 18/24 | 0.75 |
| 21 | 9:00 PM | 21/24 | 0.875 |
Simple duration calculation
When start time and end time are in the same day, calculating duration in hours is straightforward. For example, with start time of 9:00 AM and an end time of 5:00 PM, you can simply use this formula:
=end-start =5:00PM-8:00AM =0.375-0.708=.333//8hours
When times cross midnight
Calculating elapsed time is more tricky if the times cross a day boundary (midnight). For example, if the start time is 10:00 PM one day, and the end time is 5:00 AM the next day, the end time is actually less than the start time and the formula above will return a negative value, and Excel twill display a string of hash characters (########).
To correct this problem, you can use this formula for times that cross a day boundary:
=1-start+end
By subtracting the start time from 1, you get the amount of time in the first day, which you can simply add to the amount of time in the 2nd day, which is the same as the end time.
This formula won’t work for times in the same day, so we can generalize and combine both formulas inside an IF statement like so:
=IF(end>start, end-start, 1-start+end)
Now when both times are in the same day, end is greater than start time, so the simple formula is used. But when the times across a day boundary the second formula is used.
Formatting time durations
By default, Excel may display time, even time that represents a duration, using AM/PM. For example, if you have a calculated time of 6 hours, Excel may display this as 6:00 AM. To remove the AM/PM, apply a custom number format like h:mm.
In cases where calculated time exceeds 24 hours, you may want to use a custom format like [h]:mm. The square bracket syntax [h] tells Excel to display hour durations of greater than 24 hours. If you don’t use the brackets, Excel will simply “roll over” when the duration hits 24 hours (like a clock).
MOD function alternative
By using the MOD function with a divisor of 1, we can simplify the formula above to this:
=MOD(end-start,1)
Here MOD function takes care of the negative problem by using the MOD function to “flip” negative values to the required positive value. This version of the formula will handle both cases, so we can eliminate the conditional IF statement.
Note: neither formula above will handle durations greater than 24 hours. If you need this, see the date + time option below.
Simplifying the problem with date + time
You can simply the problem of calculating elapsed time by working with values that contain both date and time. To enter a date and time together, use a single space between time and date: 9/1/2016 10:00 AM
Then you can use a basic formula to calculate elapsed time:
=end-start
In the example below start and end values contain both dates and times:
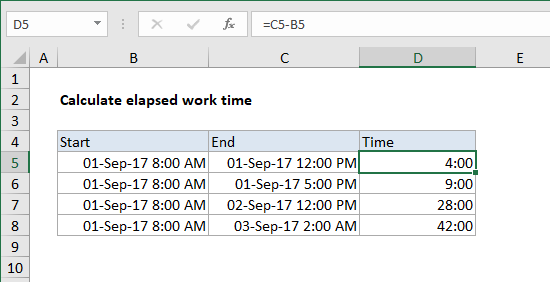
The formula is:
=C5-B5
Formatted with the custom number format [h]:mm, to display elapsed hours.