How To Perform and Interpret Regression Analysis in Excel
Examples of R Square, Significance F and P-Values, Coefficients and Residuals.
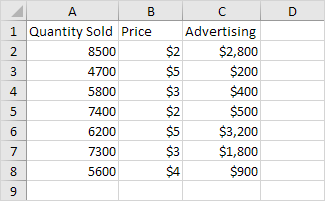
Below you can find our data. The big question is: is there a relation between Quantity Sold (Output) and Price and Advertising (Input). In other words: can we predict Quantity Sold if we know Price and Advertising?
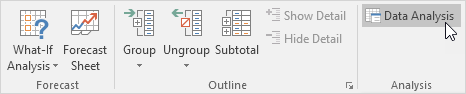
1. On the Data tab, in the Analysis group, click Data Analysis.
Note: can’t find the Data Analysis button? Click here to load the Analysis ToolPak add-in.
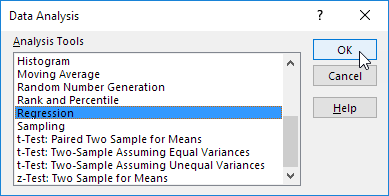
2. Select Regression and click OK.
3. Select the Y Range (A1:A8). This is the predictor variable (also called dependent variable).
4. Select the X Range(B1:C8). These are the explanatory variables (also called independent variables). These columns must be adjacent to each other.
5. Check Labels.
6. Click in the Output Range box and select cell A11.
7. Check Residuals.
8. Click OK.
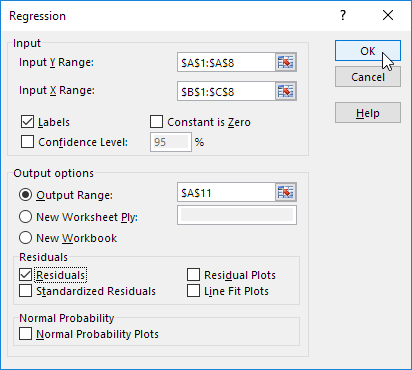
Excel produces the following Summary Output (rounded to 3 decimal places).
R Square
R Square equals 0.962, which is a very good fit. 96% of the variation in Quantity Sold is explained by the independent variables Price and Advertising. The closer to 1, the better the regression line (read on) fits the data.
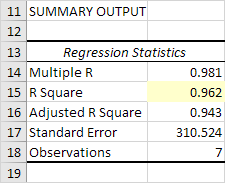
Significance F and P-values
To check if your results are reliable (statistically significant), look at Significance F (0.001). If this value is less than 0.05, you’re OK. If Significance F is greater than 0.05, it’s probably better to stop using this set of independent variables. Delete a variable with a high P-value (greater than 0.05) and rerun the regression until Significance F drops below 0.05.
Most or all P-values should be below below 0.05. In our example this is the case. (0.000, 0.001 and 0.005).
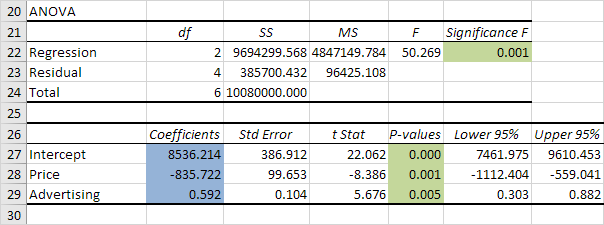
Coefficients
The regression line is: y = Quantity Sold = 8536.214 -835.722 * Price + 0.592 * Advertising. In other words, for each unit increase in price, Quantity Sold decreases with 835.722 units. For each unit increase in Advertising, Quantity Sold increases with 0.592 units. This is valuable information.
You can also use these coefficients to do a forecast. For example, if price equals $4 and Advertising equals $3000, you might be able to achieve a Quantity Sold of 8536.214 -835.722 * 4 + 0.592 * 3000 = 6970.
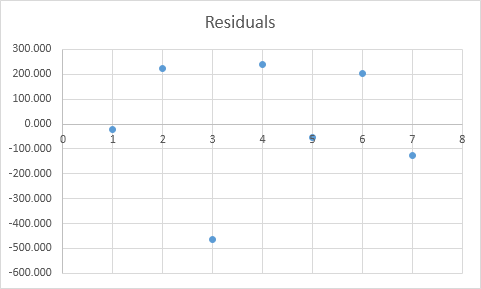
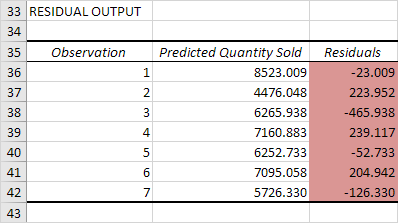
Residuals
The residuals show you how far away the actual data points are fom the predicted data points (using the equation). For example, the first data point equals 8500. Using the equation, the predicted data point equals 8536.214 -835.722 * 2 + 0.592 * 2800 = 8523.009, giving a residual of 8500 – 8523.009 = -23.009.
You can also create a scatter plot of these residuals.