How to Create Dependent Drop-down Lists in Excel
This example describes how to create dependent drop-down lists in Excel.
Here’s what we are trying to achieve:
The user selects Pizza from a drop-down list.
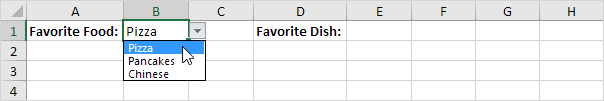
As a result, a second drop-down list contains the Pizza items.
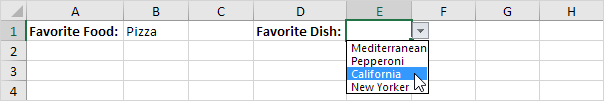
To create these dependent drop-down lists, execute the following steps.
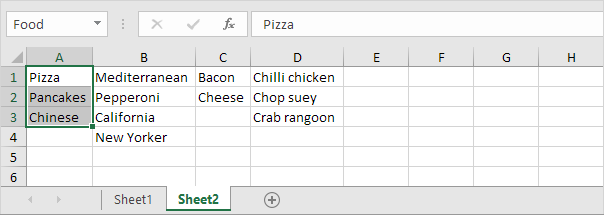
1. On the second sheet, create the following named ranges.
| Name | Range Address |
|---|---|
| Food | A1:A3 |
| Pizza | B1:B4 |
| Pancakes | C1:C2 |
| Chinese | D1:D3 |
2. On the first sheet, select cell B1.
3. On the Data tab, in the Data Tools group, click Data Validation.
The ‘Data Validation’ dialog box appears.
4. In the Allow box, click List.
5. Click in the Source box and type =Food.
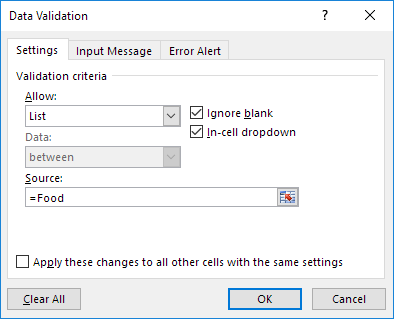
6. Click OK.
Result:
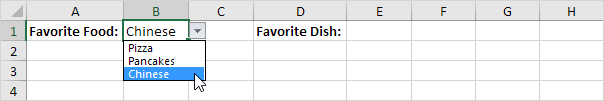
7. Next, select cell E1.
8. In the Allow box, click List.
9. Click in the Source box and type =INDIRECT($B$1).
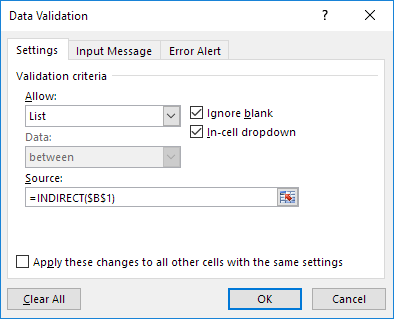
10. Click OK.
Result:
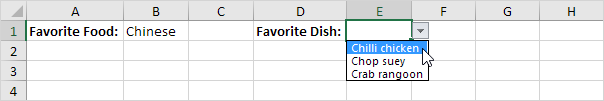
Explanation: the INDIRECT function returns the reference specified by a text string. For example, the user selects Chinese from the first drop-down list. =INDIRECT($B$1) returns the Chinese reference. As a result, the second drop-down lists contains the Chinese items.