Get employee information with VLOOKUP in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Get employee information with VLOOKUP in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=VLOOKUP(id,data,column,FALSE)
Explanation
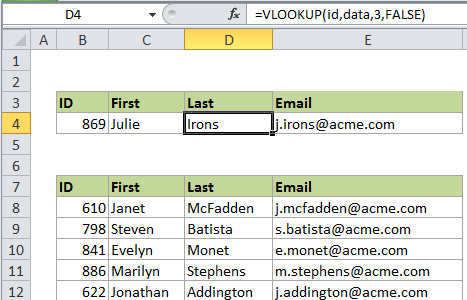
If you want to retrieve employee information from a table, and the table contains a unique id to the left of the information you want to retrieve, you can easily do so with the VLOOKUP function.
In the example shown, the VLOOKUP formula looks like this:
=VLOOKUP(id,data,3,FALSE)
How this formula works
In this case “id” is a named range = B4 (which contains the lookup value), and “data” is a named range = B8:E107 (the data in the table). The number 3 indicates the 3rd column in the table (last name) and FALSE is supplied to force an exact match.
In “exact match mode” VLOOKUP will check every value in the first column of the supplied table for the lookup value. If it finds an exact match, VLOOKUP will return a value from the same row, using the supplied column number. If no exact match is found, VLOOKUP will return the #N/A error.
Note: it’s important to require an exact match using FALSE or 0 for the last argument, which is called “range_lookup”). Otherwise, VLOOKUP might return an incorrect result.