Sum top n values in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum top n values in Excel using the example below;
To sum the top values in a range, you can use a formula based on the LARGE function, wrapped inside the SUMPRODUCT function.
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(LARGE(range,{1,2,N}))
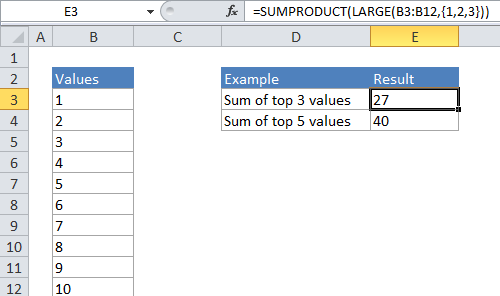
Explanation
In the generic form of the formula (above), a range of cells that contain numeric values and N represents the idea of Nth value.
In the example, the active cell contains this formula:
=SUMPRODUCT(LARGE(B4:B13,{1,2,3}))
How this formula works
In its simplest form, LARGE will return the “Nth largest” value in a range. For example, the formula:
=LARGE(B4:B13, 2)
will return the 2nd largest value in the range B4:B13 which, in the example above, is the number 9.
However, if you supply an “array constant” (e.g. a constant in the form {1,2,3}) to LARGE as the second argument, LARGE will return an array of results instead of a single result. So, the formula:
=LARGE(B4:B13,{1,2,3})
will return the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd largest value in the range B4:B13. In the example above, where B4:B13 contains the numbers 1-10, the result from LARGE will be the array {8,9,10}. SUMPRODUCT then sums the numbers in this array and returns a total, which is 27.
SUM instead of SUMPRODUCT
SUMPRODUCT is a flexible function that allows you to uses cell references for k inside the LARGE function.
However, if you are using a simple hard-coded array constant like {1,2,3} you can just use the SUM function:
=SUM(LARGE(B4:B13,{1,2,3}))
Note you must enter this formula as an array formula if you use cell references and not an array constant for k inside LARGE.
When N becomes large
When N becomes large it becomes tedious to create the array constant by hand – If you want to sum to the top 20 or 30 values in a large list, typing out an array constant with 20 or 30 items will take a long time. In this case, you can use a shortcut for building the array constant that uses the ROW and INDIRECT functions.
For example, if you want to SUM the top 20 values in a range called “rng” you can write a formula like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(LARGE(rng,ROW(INDIRECT("1:20"))))
Variable N
With insufficient data, a fixed N can cause errors. In this case, you can try a formula like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(LARGE(rng,ROW(INDIRECT("1:"&MIN(3,COUNT(rng))))))
Here, we use MIN with COUNT to sum the top 3 values, or the count of values, if less than 3.