Sum if cells contain either x or y in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if cells contain either x or y in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(--((ISNUMBER(SEARCH("cat",range1)) + ISNUMBER(SEARCH("rat",range1)))>0),range2)
Explanation
To sum if cells contain either one text string or another (i.e. contain “cat” or “rat”) you can use the SUMPRODUCT function.
Background
When you sum cells with “OR” criteria, you need to be careful not to double count when there is a possibility that both criteria will return true. In the example shown, we want to sum values in Column C when cells in column B contain either “cat” or “rat”. We can’t use SUMIFs with two criteria, because SUMIFS is based on AND logic. And if we try to use two SUMIFS (i.e. SUMIFS + SUMIFS) we will double count because there are cells that contain both “cat” and “rat”
Solution
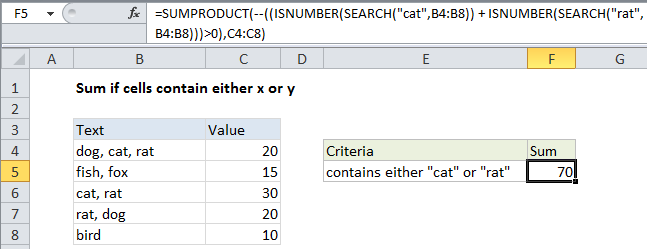
One solution is to use SUMPRODUCT with ISNUMBER + SEARCH or FIND. The formula in cell F4 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(--((ISNUMBER(SEARCH("cat",B4:B8)) + ISNUMBER(SEARCH("rat",B4:B8)))>0),C4:C8)
This formula is based the formula here that locates text inside of a cell:
ISNUMBER(SEARCH("abc",B4:B10)
When given a range of cells, this snippet will return an array of TRUE/FALSE values, one value for each cell the range. Since we are using this twice (once for “cat” and once for “rat”), we’ll get two arrays.
Next, we add these arrays together (with +), which creates a new single array of numbers. Each number in this array is the result of adding the TRUE and FALSE values in the original two arrays together. In the example shown, the array looks like this:
{2;0;2;1;0}
We need to add these numbers up, but we don’t want to double count. So we need to make sure any value greater than zero is just counted once. To do that, we force all values to TRUE or FALSE by checking the array with “>0”. This returns TRUE / FALSE:
{TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;FALSE}
Which we then convert to 1 / 0 using a double negative (–):
{1;0;1;1;0}
Case-sensitive option
The SEARCH function ignores case. If you need a sensitive option, replace SEARCH with FIND.