Sum if cells contain both x and y in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if cells contain both x and y in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMIFS(range1,range2,"*cat*",range2,"*rat*")
Explanation
To sum if cells contain both x and y (i.e. contain “cat” and “rat”, in the same cell) you can use the SUMIFS function.
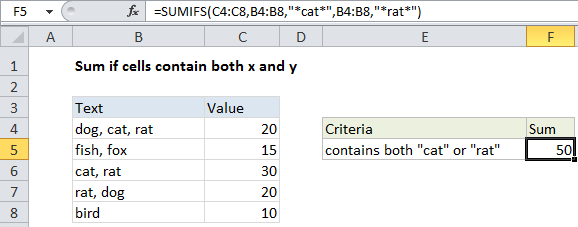
In the example shown, the formula in F5 is:
=SUMIFS(C4:C8,B4:B8,"*cat*",B4:B8,"*rat*")
How this formula works
The SUMIFS function is based on AND logic and this behavior is automatic. We just need to supply two range/criteria pairs, both operating on the same range (B4:B11).
For both criteria (contains “rat”, contains “cat”) we use an asterisk, which is a wildcard that matches “one or more characters”. We put an asterisk at the start and end to allow the formula to match “cat” and “rat” wherever they appear in the cell.
When both criteria return TRUE in the same row, SUMIFS sums the value in column C.
Note that SUMIFs is not case-sensitive.