Running count group by n size in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Running count group by n size in Excel using the example below;
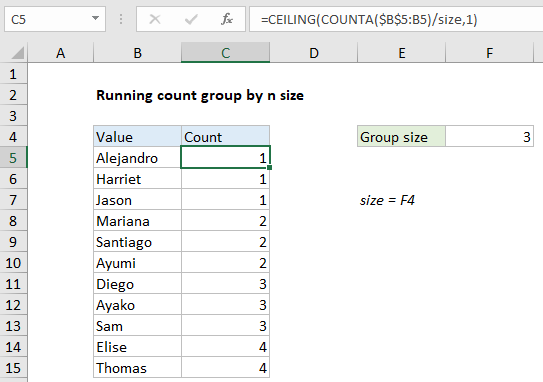
Formula
=CEILING(COUNTA(expanding_range)/size,1)
>
Explanation
To creating a running count of groups of a variable size, you can use the COUNTA and CEILING function. In the example shown, C5 contains this formula:
=CEILING(COUNTA($B$5:B5)/size,1)
where “size” is the named range F4.
How this formula works
The core of this formula is the COUNTA function, configured with an expanding range like this:
COUNTA($B$5:B5)
As the formula is copied down the column, the range starting with B5 expands to include each new row, and COUNTA returns a running count of all non-blank entries in the range.
The result of COUNTA is then divided by “size”, configured as a named range F4. Using a cell on the worksheet for group size allows the grouping to be changed at any time without editing the formula. The named range is used only for readability and convenience.
The resulting value is then processed by the CEILING function, with a significance of 1. CEILING is a rounding function that always rounds up to the next unit of significance. In this example, this causes fractional values to be rounded up to the next integer.
Handling empty cells
If the range you are counting contains blank or empty cells, you can wrap the formula inside the IF function like this:
=IF(B5<>"",CEILING(COUNTA($B$5:B5)/size,1),"")
Here, we run the counting and rounding operation described above only when the cell in column B is not blank. If it is blank, we skip the count and return an empty string.