Basic outline numbering in Excel
This tutorial shows how to create 1st and 2nd level outline formatting using excel formulas.
To generate basic outline numbering you can use COUNTA, MID, FIND, IF, and LEN functions.
Note: The formula used will only handle a 2-level outline.
Explanation
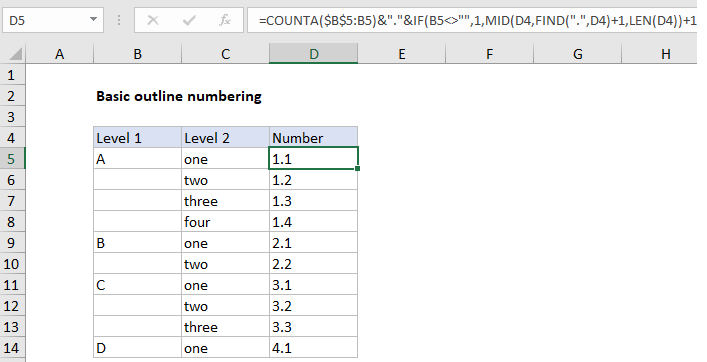
In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=COUNTA($B$5:B5)&"."&IF(B5<>"",1,
MID(D4,FIND(".",D4)+1,LEN(D4))+1)
How this formula works
At the core, this formula builds a level 1 and level 2 number and concatenates the two numbers together with a period (“.”) as a separator. The result is a value like “1.1”. The “level 1” number is generated with COUNTA like this:
=COUNTA($B$5:B5)
Note the range is an expanding reference, so it will expand as it is copied down the column.
The “level 2” number is generated with this code:
IF(B5<>"",1,MID(D4,FIND(".",D4)
+1,LEN(D4))+1)
Step 1: Here, the IF function is used to check the contents of B5. If B5 is not blank, it means we have a new level 1 heading and IF returns 1. In other words, every time we have a new level 1 entry, we restart level 2 numbering at 1.
Step 2: If the B5 *is* blank we need to increment the level 2 number using the value in the cell above. This is a bit tricky, because the outline number is a text string, not a number. That means we need to extract the value with a text function before we can increment. To do this, we use the MID function to extract all text to the right of the period (“.”), which we locate with the FIND function:
MID(D4,FIND(".",D4)+1,LEN(D4))+1
Step 3:The LEN function is used as a simple way to guarantee all characters after the period are extracted. Notice we then add 1 directly to the result, which is still text. This math operation causes Excel to coerce the text to a number, so the result is an incremented number. Finally, the level 1 and level 2 numbers are concatenated together with a period (“.”) as a separator.