Understanding VBA Function and Sub in Excel
Excel Visual Basic: A set of commands to perform a specific task is placed into a procedure, which can be a Function procedure or a Sub procedure (also known as functions and subroutines).
The difference between a function and a sub in Excel VBA is that a function can return a value while a sub cannot. Functions and subs become very useful as program size increases.
Therefore, if you wish to perform a task that returns a result (e.g. summing of a group of numbers), you will generally use a Function procedure, but if you just need a set of actions to be carried out (e.g. formatting a set of cells), you might choose to use a Sub procedure.
Function
If you want Excel VBA to perform a task that returns a result, you can use a function. Place a function into a module (In the Visual Basic Editor, click Insert, Module). For example, the function with name Area.
Function Area(x As Double, y As Double) As Double
Area = x * y
End Function
Explanation: This function has two arguments (of type Double) and a return type (the part after As also of type Double). You can use the name of the function (Area) in your code to indicate which result you want to return (here x * y).
You can now refer to this function (in other words call the function) from somewhere else in your code by simply using the name of the function and giving a value for each argument.
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim z As Double
z = Area(3, 5) + 2
MsgBox z
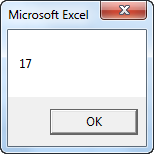
Explanation: The function returns a value so you have to ‘catch’ this value in your code. You can use another variable (z) for this. Next, you can add another value to this variable (if you want). Finally, display the value using a MsgBox.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Sub
If you want Excel VBA to perform some actions, you can use a sub. Place a sub into a module (In the Visual Basic Editor, click Insert, Module). For example, the sub with name Area.
Sub Area(x As Double, y As Double)
MsgBox x * y
End Sub
Explanation: This sub has two arguments (of type Double). It does not have a return type! You can refer to this sub (call the sub) from somewhere else in your code by simply using the name of the sub and giving a value for each argument.
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code line:
Area 3, 5
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
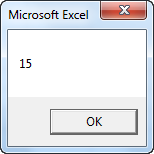
Can you see the difference between the function and the sub? The function returned the value 15. We added the value 2 to this result and displayed the final result. When we called the sub we had no more control over the result (15) because a sub cannot return a value!
