Split dimensions into two parts in Excel Worksheet
If you have worksheet that contains text dimensions (i.e. “50 ft x 200 ft” etc.) you can split the into two parts with formulas that use several text functions.
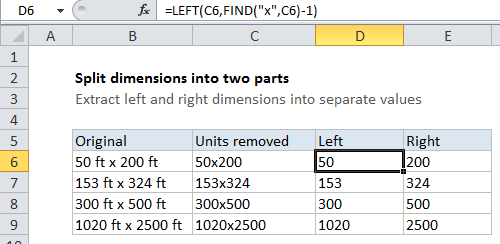
Explanation
Background
A common annoyance with data is that it may be represented as text instead of numbers. This is especially common with dimensions, which may appear in one text string that includes units, for example:
50 ft x 200 ft
153 ft x 324 ft
Etc.
In a spreadsheet, it’s a lot more convenient to have actual numbers so that you can use them in calculations as you wish.
Extracting individual dimensions from a text representation can be done with formulas that combine several text functions.
Solution
In this case, it because we have both the “ft” unit and space characters (” “) included in the dimensions, it makes sense to remove these first. That will “normalize” the dimensions and simplify the formulas that do the actual extraction.
To remove both “ft” and ” “, we are using this formula in cell C6, which contains two nested SUBSTITUTE functions:
=SUBSTITUTE(SUBSTITUTE(B5,"ft","")," ","")
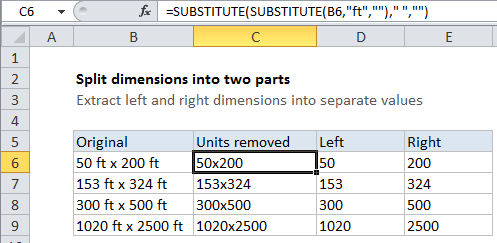
This formula takes the original text, and first strips “ft” (in the inner ), then strips spaces with the outer SUBSTITUTE function.
The result is a dimension with just the “x” separating the two parts.
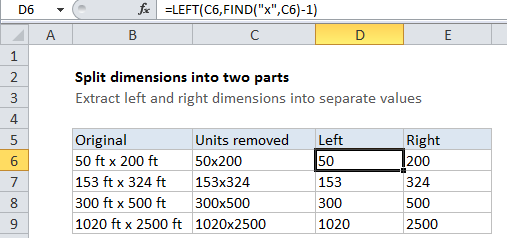
Now we can two relatively straightforward formulas to extract each part. To get the dimension on the left, D6 contains:
=LEFT(C5,FIND("x",C5)-1)
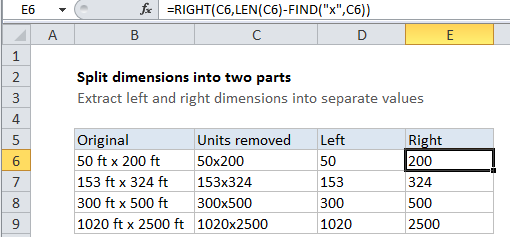
To get the dimension on the right, E6 contains:
=RIGHT(C5,LEN(C5)-FIND("x",C5))
Both of the formulas above extract the correct dimension by using FIND to locate the “x”. For more detail, see the related function links on this page.