Basic numeric sort formula in Excel
To dynamically sort data that contains only numeric values, you can use a helper column and a formula created with the RANK and COUNTIF functions.
Formula
=RANK(A1,values)+COUNTIF(exp_rng,A1)-1
Note: this formula is the set-up for a formula that can extract and display data using a predefined sort order in a helper column. One example here.
Explanation
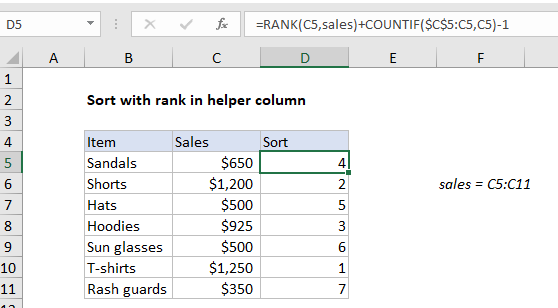
In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=RANK(C5,sales)+COUNTIF($C$5:C5,C5)-1
where “sales” is the named range C5:C11
How this formula works
The core of this formula is the RANK function, which is used to generate a rank of sales values, where the highest number is ranked #1:
=RANK(C5,sales)
Here, RANK uses the named range “sales” (C5:C11) for convenience. By default, RANK will assign 1 to the highest value, 2 to the second highest value, and so on. This works perfectly as long as numeric values are unique. However, to handle numeric values which contain duplicates, we need to use the COUNTIF function to break ties. This is done by adding the result of this snippet to the value returned by RANK:
COUNTIF($C$5:C5,C5)-1
Notice the range is entered as a mixed reference that will expand as the formula is copied down the table. As written, this reference will include the current row, so we subtract 1 to “zero out” the first occurrence. This means the expression will return zero for each numeric value until a duplicate is encountered. At the second instance, the expression will return 1, at the third instance, it will return 2, and so on. This effectively breaks ties, and allows the formula to generate a sequential list of numbers with no gaps.
Once the formula is in place, data can be sorted by the helper column. It can also be retrieved with INDEX using the values in the helper column.