How to use Excel INDIRECT Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the INDIRECT function with syntax and examples.
Excel INDIRECT function Description
Microsoft Excel INDIRECT function returns the reference to a cell based on its string representation.
The INDIRECT function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Lookup/Reference Function that can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
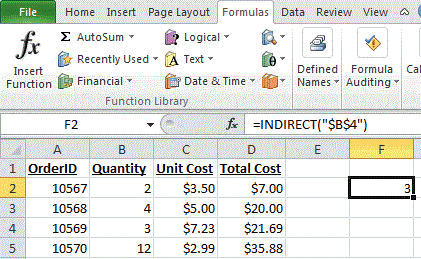
Explanation: Based on the example above, the INDIRECT function would return:
=INDIRECT("$B$4")
Result: 3
=INDIRECT("A5")
Result: 10570
=INDIRECT("A5", TRUE)
Result: 10570
=INDIRECT("R2C3", FALSE)
Result: $3.50
Syntax
The syntax for the INDIRECT function in Microsoft Excel is:
INDIRECT( string_reference, [ref_style] )
Arguments
- string_reference
- A textual representation of a cell reference.
- ref_style
- Optional. It is either a TRUE or FALSE value. TRUE indicates that string_reference will be interpreted as an A1-style reference. FALSE indicates that string_reference will be interpreted as an R1C1-style reference. If this parameter is omitted, it will interpret string_reference as an A1-style.
Returns
The INDIRECT function returns the reference to a cell and thus displays the referenced cell’s value.