Invoice status with nested if in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate Invoice status with nested if in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=IF(balance=0,"Paid",IF(current_date<due_date,"Open","Overdue"))
Explanation
To determine invoice status (i.e. paid, open, overdue), you can use a nested IF formula and the TODAY function.
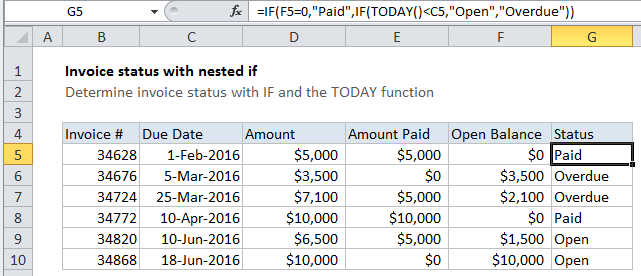
In the example shown, the formula in G5 is:
=IF(F5=0,"Paid",IF(TODAY()<C5,"Open","Overdue"))
How this formula works
Note: the “current date” (i.e. today) for this example is May 31, 2016
With nested IF statements, the flow is from outer IF statements to inner IF statements, and the challenge is always to construct the flow so that the formula returns a logically correct result.
Here, the outermost IF tests first to see if the balance is zero:
=IF(F5=0
If TRUE, the formula returns “Paid”.
If not, the result of the first IF is FALSE, and another IF statement is run. This one checks to see if TODAY() is less than the due date in column C:
IF(TODAY()<C5
If TRUE, the formula returns “Open”.
If FALSE, the formula returns “Overdue”.