Tax rate calculation with fixed base in Excel
This tutorial shows how to work Tax rate calculation with fixed base in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=IF(A1<limit,A1*rate,(A1-limit)*rate+fixed)
Explanation
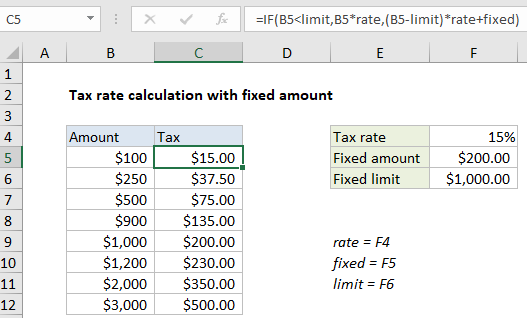
This example shows how to set up simple formula using the IF function to calculate a tax amount with both fixed and variable components. In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=IF(B5<limit,B5*rate,(B5-limit)*rate+fixed)
in a worksheet with the following named ranges: rate = F4, fixed = F5, limit = F6.
The rules of this problem are as follows:
- If amount is less than $1000, tax is amount * 20%.
- If amount is greater than or equal to $1000, tax is $200 + (amount over 1000) *20%
How this formula works
The core of this formula is a single IF statement that checks the amount in column B against the base limit:
=IF(B5<limit
If TRUE, the formula simply multiplies the amount in B5 by tax rate:
B5*rate
If FALSE, the formula applies the tax rate to the amount over 1000, then adds the fixed amount:
(B5-limit)*rate+fixed)