How to calculate annual compound interest schedule in Excel
To calculate annual compound interest, you can use a formula based on the starting balance and annual interest rate.
Formula
=start+(start*rate)
Explanation
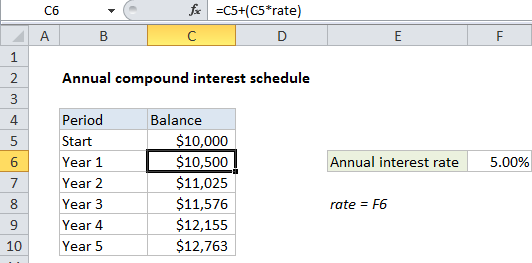
In the example shown, the formula in C6 is:
=C5+(C5*rate)
Note: “rate” is the named range F6.
How this formula works
If you have an annual interest rate, and a starting balance you can calculate interest with:
=balance * rate
and the ending balance with:
=balance+(balance*rate)
So, for each period in the example, we use this formula copied down the table:
=C5+(C5*rate)
With the FV function
The FV function can also be used to calculate future value. The equivalent formula is:
=FV(rate,1,0,-C5)
The interest rate is used as-is, since we are compounding annually, nper is 1, since there is only one period per year, pmt is zero, since there are no additional payments, and pv is the starting balance, input as a negative value by convention.