Example of Future value of annuity in Excel
To get the present value of an annuity, you can use the PV function.
Formula
=FV(rate,periods,payment)
Explanation
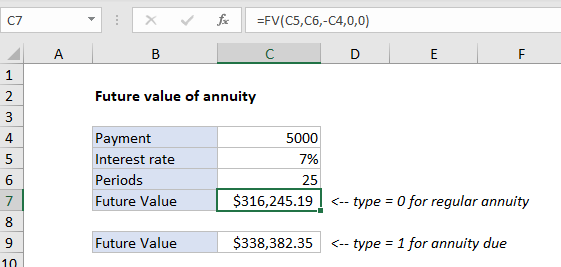
In the example shown, the formula in C7 is:
=FV(C5,C6,-C4,0,0)
Explanation
An annuity is a series of equal cash flows, spaced equally in time. In this example, a $5000 payment is made each year for 25 years, with an interest rate of 7%. To calculate future value, the PV function is configured as follows:
- rate – the value from cell C5, 7%.
- nper – the value from cell C6, 25.
- pmt – the value from cell C4, 100000.
- pv – 0.
- type – 0, payment at end of period (regular annuity).
With this information, the future value of the annuity is $316,245.19. Note payment is entered as a negative number, so the result is positive.
Annuity due
An annuity due is a repeating payment made at the beginning of each period, instead of at the end of each period. In Excel’s FV function, set the type argument to 1 for an annuity due:
=FV(C5,C6,-C4,0,1)
With type set to 1, FV returns $338,382.35.