Sum race time splits in Excel
If you need to add up (sum) up race time splits that are some combination of hours, minutes, and seconds, you can simply use the SUM function.
However, you must take care to enter times with the right syntax and use a suitable time format to display results, as explained below.
Formula
=SUM(range)
Explanation
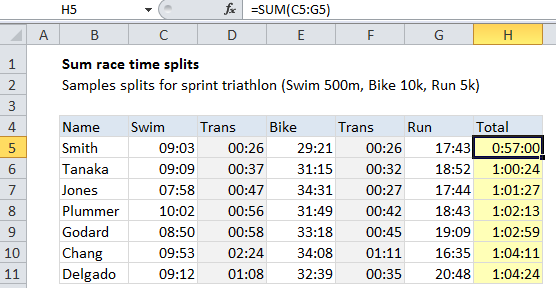
The formula in cell H5 is:
=SUM(C5:G5)
Enter times in correct format
You must be sure that times are correctly entered in hh:mm:ss format. For example, to enter a time of 9 minutes, 3 seconds, type: 0:09:03
Excel will show the time in the formula bar as 12:09:03 AM, but will record the time properly as a decimal value.
Internally, Excel tracks times as decimal numbers, where 1 hour = 1/24, 1 minute = 1/(24*60), and 1 second = 1/(24*60*60). How Excel displays time depends on what number format is applied.
Use a suitable time format
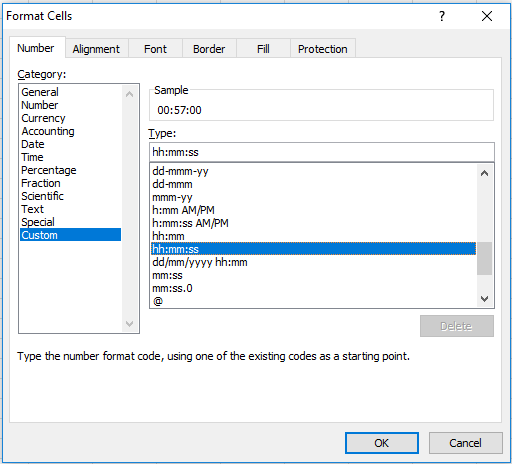
When working with times, you must take care to use a time format that makes sense to display times that represent durations.
To access and apply custom time formats, select the cell(s), then use Control + 1 (Command + 1 on a Mac), then Number > Custom.
These are the number formats used in the example shown:
mm:ss // split times h:mm:ss // total time
If total times may exceed 24 hours, use this format:
[h]:mm:ss
The square bracket syntax tells Excel not to “roll over” times greater than 24 hours.