How to get number of days, weeks, months or years between two dates in Excel
To get the number of days, weeks or years between two dates in Excel, use the DATEDIF function. The DATEDIF function has three arguments.
1. Fill in “d” for the third argument to get the number of days between two dates.
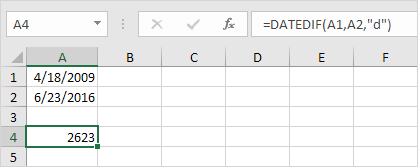
Note: =A2-A1 produces the exact same result!
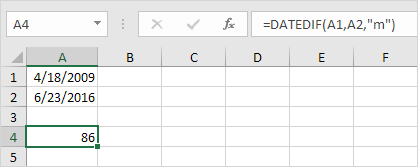
2. Fill in “m” for the third argument to get the number of months between two dates.
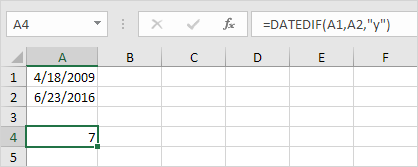
3. Fill in “y” for the third argument to get the number of years between two dates.
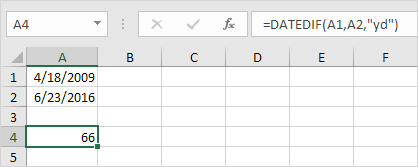
4. Fill in “yd” for the third argument to ignore years and get the number of days between two dates.
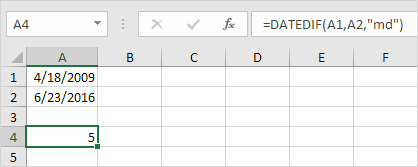
5. Fill in “md” for the third argument to ignore months and get the number of days between two dates.
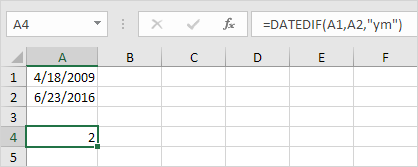
6. Fill in “ym” for the third argument to ignore years and get the number of months between two dates.
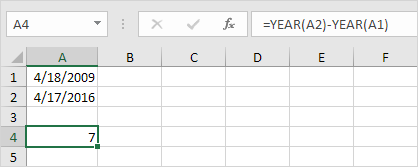
Important note: the DATEDIF function returns the number of complete days, months or years. This may give unexpected results when the day/month number of the second date is lower than the day/month number of the first date. See the example below.
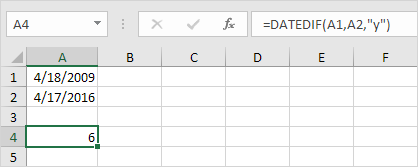
The difference is 6 years. Almost 7 years! Use the following formula to return 7 years.