Create date range from two dates in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Create date range from two dates in Excel using example below.
To display a date range in one cell based on dates in different cells, you can use a formula based on the TEXT function.
Formula
=TEXT(date1,"format")&" - "&TEXT(date2,"format")
Explanation
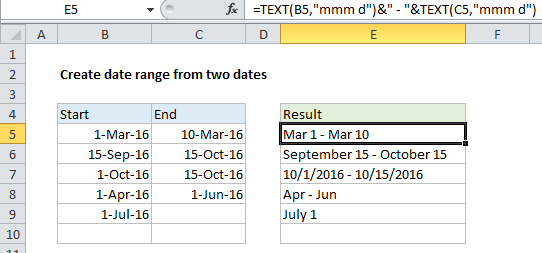
In the example shown, the formula in cell E5 is:
=TEXT(B5,"mmm d")&" - "&TEXT(C5,"mmm d")
How this formula works
The TEXT function takes numeric values and converts them to text values using the format you specify. In this example, we are using the format “mmm d” for both TEXT functions in E5. The results are joined with a hyphen using simple concatenation.
Note: the other examples in column E all use different text formats.
End date missing
If the end date is missing, the formula won’t work correctly because the hyphen will still be appended to the start date (e.g.”March 1 – “).
To handle this case, you can wrap the concatenation and second TEXT function inside IF like so:
=TEXT(date1,"mmm d")&IF(date2<>""," - "&TEXT(date2,"mmm d"),"")
This creates the full date range when both dates are present, but outputs only the start date when the end date is missing.
Start date missing
To handle a case where both dates are missing, you could nest another IF like this:
=IF(date1<>"",TEXT(date1,"mmmm d")&IF(date2<>""," - "&TEXT(date2,"mmm d"),""),"")
This formula simply returns an empty string (“”) when date1 is not available.