Count cells less than in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count cells less than in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=COUNTIF(range,”<X”)
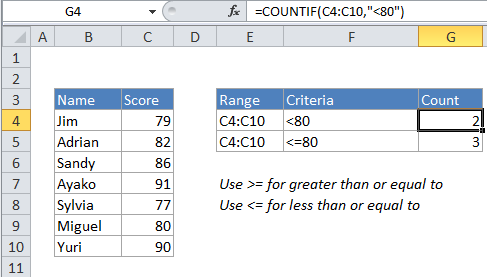
Explanation
To count the number of cells that contain values less than a particular number, you can use the COUNTIF function. In the generic form of the formula (above) rng represents a range of cells that contain numbers, and X represents the boundary below which you want to count.
In the example, the active cell contains this formula:
=COUNTIF(C4:C10,"<80")
How this formula works
COUNTIF counts the number of cells in the range that contain numeric values less than X and returns the result as a number.
If you want to count cells that are less than or equal to 80, use:
=COUNTIF(C4:C10,"<=80")
If you want to use a value in another cell as part of the criteria, use the ampersand (&) character to concatenate like this:
=COUNTIF(range,"<"&a1)
If the value in cell a1 is “100”, the criteria will be “<100” after concatenation.