Sum if greater than in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if greater than in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMIF(range,">1000")
Explanation
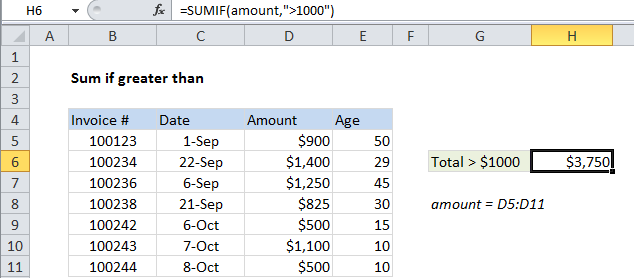
To sum if greater than, you can use the SUMIF function.
In the example shown, cell H6 contains this formula:
=SUMIF(amount,">1000")
Where “amount” is a named range for cells D5:D11.
This formula sums the amounts in column D when they are greater than 1000.
How the formula works
The SUMIF function supports Excel’s logical operators (i.e. “=”,”>”,”>=”, etc.), so you can use these as you like in your criteria.
In this case, we want to match amounts greater than 1000, and the “criteria range” is the same as the “sum range” so there is no need to enter the sum range as a final argument.
The SUMIF function simply sums up all amounts greater than 1000.
Note that both the operator (>) and threshold amount are enclosed in double quotes (“”).
If you want to include the threshold number in the sum, use greater than or equal to (>=), like so:
=SUMIF(amount,">=1000")
Using a cell reference
If you want to expose the threshold amount on the worksheet so that it can be easily changed, use this formula:
=SUMIF(range,">"&A1)
Where A1 is a reference to a cell that contains the threshold number.
Alternative with SUMIFS
You can also use the SUMIFS function. SUMIFS can handle multiple criteria, but the order of the arguments is different from SUMIF. The equivalent SUMIFS formula is:
=SUMIFS(amount,amount,">1000")
Notice that the sum range always comes first in the SUMIFS function. Also note that SUMIFS criteria need to be entered in pairs (range / criteria) which means the named range “amount” must be entered twice: once as the sum range, and once as a criteria range.