nth smallest value with criteria in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate nth smallest value with criteria in Excel using the example below;
To get the 2nd smallest value, 3rd smallest value, 4th smallest value, and so on, where each value matches supplied criteria, you can use an array formula that uses the SMALL and IF functions.
Formula
{=SMALL(IF(criteria,values),n)}
Explanation
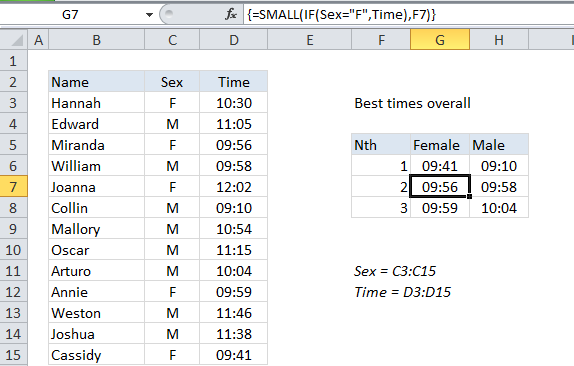
In the example shown, the formula in G7 is:
{=SMALL(IF(Sex="F",Time),F7)}
Where “Sex” is a named range for C3:C15 and “Time” is the named range D3:D15.
Note: this is an array formula and must be entered using Control + Shift + Enter.
How this formula works
The SMALL function is fully automatic — you just need to supply a range and an integer for”nth” to specify the ranked value you want.
The problem in this case is that we don’t want SMALL to operate on every value in the range, just values that are either male or female (M or F). To apply this criteria, we use the IF function, which provides a logical test for either “M” or ‘F”. Because we are applying the test to an array of values, the result will also be an array. In the example shown, the resulting array looks like this:
{0.00729166666666667;FALSE;0.00689814814814815;FALSE;0.00835648148148148;FALSE; FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;0.00693287037037037;FALSE;FALSE;0.00672453703703704}
Where FALSE represents male times and numbers represent female times. (Times like this are fractional values, which is why we have so many decimal places for some times).
The SMALL function will automatically ignore TRUE and FALSE values, so the result will be the nth smallest value from the set of actual numbers in the array.
Error with no nth
You’ll get an error if there is no nth smallest value based on supplied criteria. You can trap this error with IFERROR and replace with whatever value makes sense like this:
{=IFERROR(SMALL(IF(Sex="F",Time),F8),"-")}
Multiple criteria
To handle multiple criteria, you can extend the formula with boolean logic in a form like this:
=SMALL(IF((criteria1)*(criteria2),values),n)
Where criteria1 and criteria2 and represent an expression to test values in a criteria range, as shown in the original example above.