Count cells between dates in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count cells between dates in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=COUNTIFS(range,">="&date1,range,"<="&date2)
Explanation
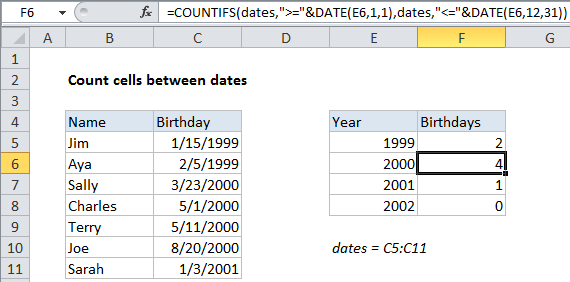
To count the number of cells that contain dates between two dates, you can use the COUNTIFS function. In the example shown, F5 contains this formula:
=COUNTIFS(dates,">="&DATE(E5,1,1),dates,"<="&DATE(E5,12,31))
This formula counts birthdays in the year 2000, that appear in the range C5:C11.
Note: this formula uses the named range “dates”, C5:C11.
How this formula works
The COUNTIFS function is built to count cells that meet multiple criteria. In this case, we need to provide two criteria: one criteria for the earlier date and one for the later date. We supply the named range dates (C5:C11) for both criteria.
To construct each date, we use the DATE function:
DATE(E5,1,1) // build first day of year DATE(E5,12,31) // build last day of year
The DATE function makes it easy to build dates based on year, month, and day arguments that are either hard-coded or supplied as cell references. In the example, month and day are hard-coded, and we get year from column E.
Note: the operators “>=” and “<=” must be entered as text and surrounded by double quotes. This means we must use concatenation (&) to join each operator to each date.