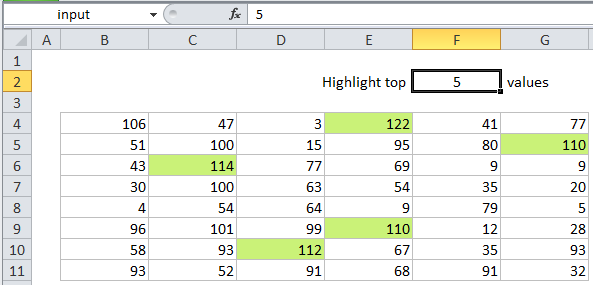
Highlight top values in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Highlight top values in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=A1>=LARGE(data,N)
Explanation
To highlight the highest values in a set of data with conditional formatting, you can use a formula based on the LARGE function.
In the example shown, the formula used for conditional formatting is:
=B4>=LARGE(data,input)
Note: Excel contain a conditional formatting “preset” that highlights top values. However, using a formula instead provides more flexibility.
How this formula works
This formula uses two named ranges: data (B4:G11) and input (F2). These are for readability and convenience only. If you don’t want to use named ranges, make sure you use absolute references for both of these ranges in the formula.
This formula is based on the LARGE function, which returns the nth largest value from a range or array of values. The range appears as the first argument in LARGE, and the value for “n” appears as the second:
LARGE(data,input)
In the example, the input value (F2) is 5, so LARGE will return the 5th largest value in the data, which is 110. The formula then compares each value in the data range with 110, using the greater than or equal to operator:
=B4>=LARGE(data,input) =B4>=110
Any cell with a value greater than or equal to 110 triggers the rule, and the conditional formatting is applied.