How to translate letters to numbers in Excel
To translate letters in a string to numbers, you can use an array formula based on the TEXTJOIN and VLOOKUP functions, with a defined translation table to provide the necessary lookups.
Formula
{=TEXTJOIN("",1,VLOOKUP(T(IF(1,MID(A1,ROW
(INDIRECT("1:"&LEN(A1))),1))),xtable,2,0))}
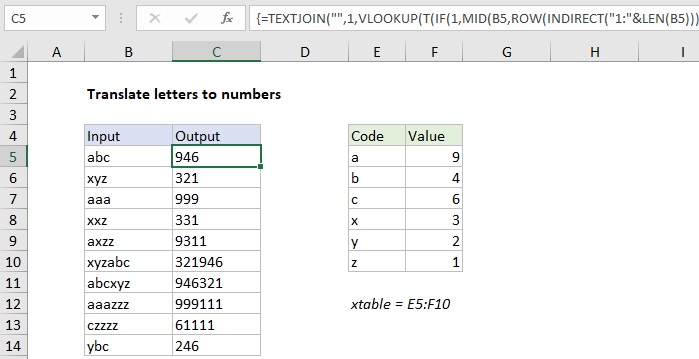
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
{=TEXTJOIN("",1,VLOOKUP(T(IF(1,MID(B5,ROW
(INDIRECT("1:"&LEN(B5))),1))),xtable,2,0))}
where “xtable” is the named range E5:F10.
Note: this is an array formula and must be entered with control + shift + enter.
How this formula works
At the core, this formula uses an array operation to generate an array of letters from the input text, translates each letter individually to a number, then joins all numbers together again and returns the output as a string.
To parse the input string into an array or letters, we use MID, ROW, LEN and INDIRECT functions like this:
MID(B5,ROW(INDIRECT("1:"&LEN(B5))),1)
LEN returns the length of the input text, which is concatenated to “1:” and handed off to INDIRECT as text. INDIRECT evaluates the text as a row reference, and the ROW function returns an array of numbers to MID:
MID(B5,{1;2;3},1)
MID then extracts one character for at each starting position and we have:
=TEXTJOIN("",1,VLOOKUP(T(IF(1,{"a";"b";"c"})),xtable,2,0))
Essentially, we are asking VLOOKUP to find a match for “a”, “b”, and “c” at the same time. For obscure reasons, we need to “dereference” this array in a particular way using both the T and IF functions. After VLOOKUP runs, we have:
=TEXTJOIN("",1,{9;4;6})
and TEXTJOIN returns the string “946”. If you need a number as final result, add zero. The math operation will coerce the text into a number.
Note: the TEXTJOIN function was introduced via the Office 365 subscription program in 2018.