Two-way lookup with VLOOKUP in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate Two-way lookup with VLOOKUP in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value,table,MATCH(col_name,col_headers,0),0)
Explanation
Note:
Inside the VLOOKUP function, the column index argument is normally hard-coded as a static number. However, you can also create a dynamic column index by using the MATCH function to locate the right column. This technique allows you to create a dynamic two-way lookup, matching on both rows and columns. It can also make a VLOOKUP formula more resilient: VLOOKUP can break when columns are inserted or removed from a table, but a formula with VLOOKUP + MATCH can continue to work correctly even changes are made to columns.
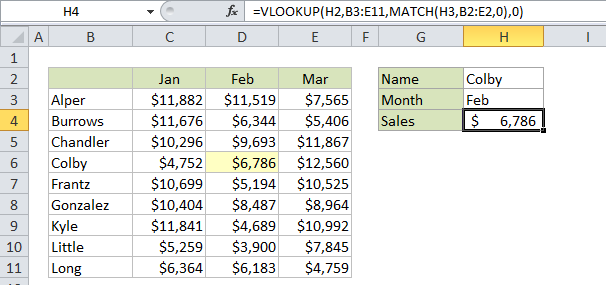
Example
In the example, we are using this formula to dynamically lookup both rows and columns with VLOOKUP:
=VLOOKUP(H2,B3:E11,MATCH(H3,B2:E2,0),0)
H2 supplies the lookup value for the row, and H3 supplies the lookup value for the column.
How this formula works
This is a standard VLOOKUP exact match formula with one exception: the column index is supplied by the MATCH function.
Note that the lookup array given to MATCH (B2:E2) representing column headers deliberately includes the empty cell B2. This is done so that the number returned by MATCH is in sync with the table used by VLOOKUP. In other words, you need to give MATCH a range that spans the same number of columns VLOOKUP is using in the table. In the example (for Feb) MATCH returns 3, so after MATCH runs, the VLOOKUP formula looks like this:
=VLOOKUP(H2,B3:E11,3,0)
Which returns sales for Colby (row 4) in Feb (column 3), which is $6,786.