Calculate cumulative loan principal payments in Excel
To calculate the cumulative principal paid between any two loan payments, you can use the CUMPRINC function.
Formula
=CUMPRINC(rate,nper,pv,start,end,type)
Explanation
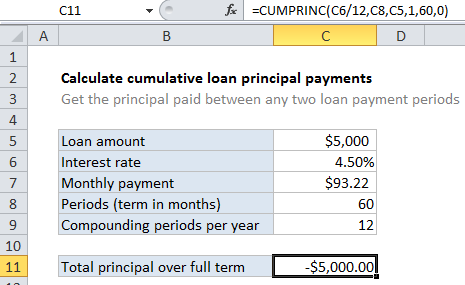
In the example shown, we calculate the total principal paid over the full term of the loan by using the first and last period. The formula in C10 is:
=CUMPRINC(C6/12,C8,C5,1,60,0)
How this formula works
For this example, we want to calculate cumulative principal payments over the full term of a 5-year loan of $5,000 with an interest rate of 4.5%. To do this, we set up CUMPRINC like this:
rate – The interest rate per period. We divide the value in C6 by 12 since 4.5% represents annual interest:
=C6/12
nper – the total number of payment periods for the loan, 60, from cell C8.
pv – The present value, or total value of all payments now, 5000, from cell C5.
start_period – the first period of interest, 1 in this case, since we are calculating principal across the entire loan term.
end_period – the last period of interest, 60 in this case for the full loan term.
With these inputs, the CUMPRINC function returns 5,000, which matches the original loan value as expected.