How to calculate months between dates in Excel
To calculate months between two dates as a whole number, you can use the DATEDIF function.
Formula
=DATEDIF(start_date,end_date,"m")
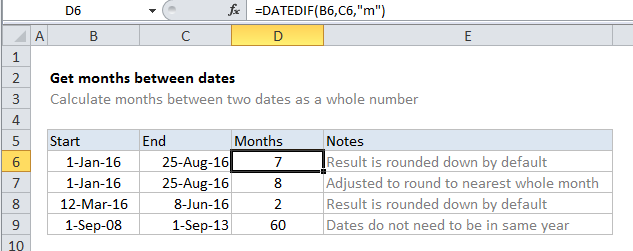
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in D6 is:
=DATEDIF(B6,C6,"m")
Note that the DATEDIF automatically rounds down. To round up to the nearest month, see below.
The mystery of DATEDIF
The DATEDIF function is a “compatibility” function that comes from Lotus 1-2-3. For reasons unknown, DATEDIF is only documented in Excel 2000, and will not appear as a suggested function in the formula bar. However, you can use DATEDIF in all Excel versions since that time, you just need to enter the function manually. Excel will not help you with function arguments.
How this formula works
DATEDIF takes 3 arguments: start date, end_date, and unit. In this case, we want months, so we supply “m” for unit.
DATEDIF automatically calculates and returns a number for months, rounded down.
Nearest whole month
If you want to calculate months to the nearest whole month, you can make a simple adjustment to the formula:
=DATEDIF(start_date,end_date+15,"m")
This ensures that end dates occurring in the 2nd half of the month are treated like dates in the following month, effectively rounding up the final result.