Extract time from a date and time in Excel
This tutorial show how to Extract time from a date and time in Excel using the example below.
If you have dates with time values and you want to extract only the time portion (the fractional part), you can use a formula that uses the MOD function.
Note: Excel handles dates and time using a scheme in which dates are serial numbers and times are fractional values. For example, June 1, 2000 12:00 PM is represented in Excel as the number 36678.5, where 36678 is the date and .5 is the time.
Formula
=MOD(date,1)
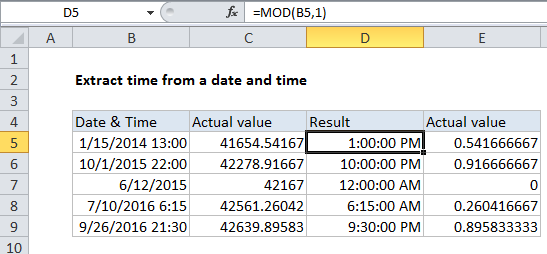
Explanation of how this formula works
Assuming A1 contains the date and time value June 1, 2000 12:00 PM, the formula below will return just the time portion (.5):
=MOD(A1,1)
The MOD function returns the remainder from division. The first argument is the number and the second is the divisor. Here are a few examples:
=MOD(5,2) // returns 1 =MOD(7,5) // returns 2
So, if you use MOD with a divisor of 1, the result will be the fractional part of the number, if any, because every whole number can be evenly divided by itself. For example:
=MOD(3.125,1) // returns 0.125
In short, =MOD(number,1) returns just the fractional part of a number, discarding the integer portion, so it’s a convenient way to extract time from a date and time.
Note: if you use this formula to strip the time from a date + time, you’ll need to adjust the number format to a suitable time format.